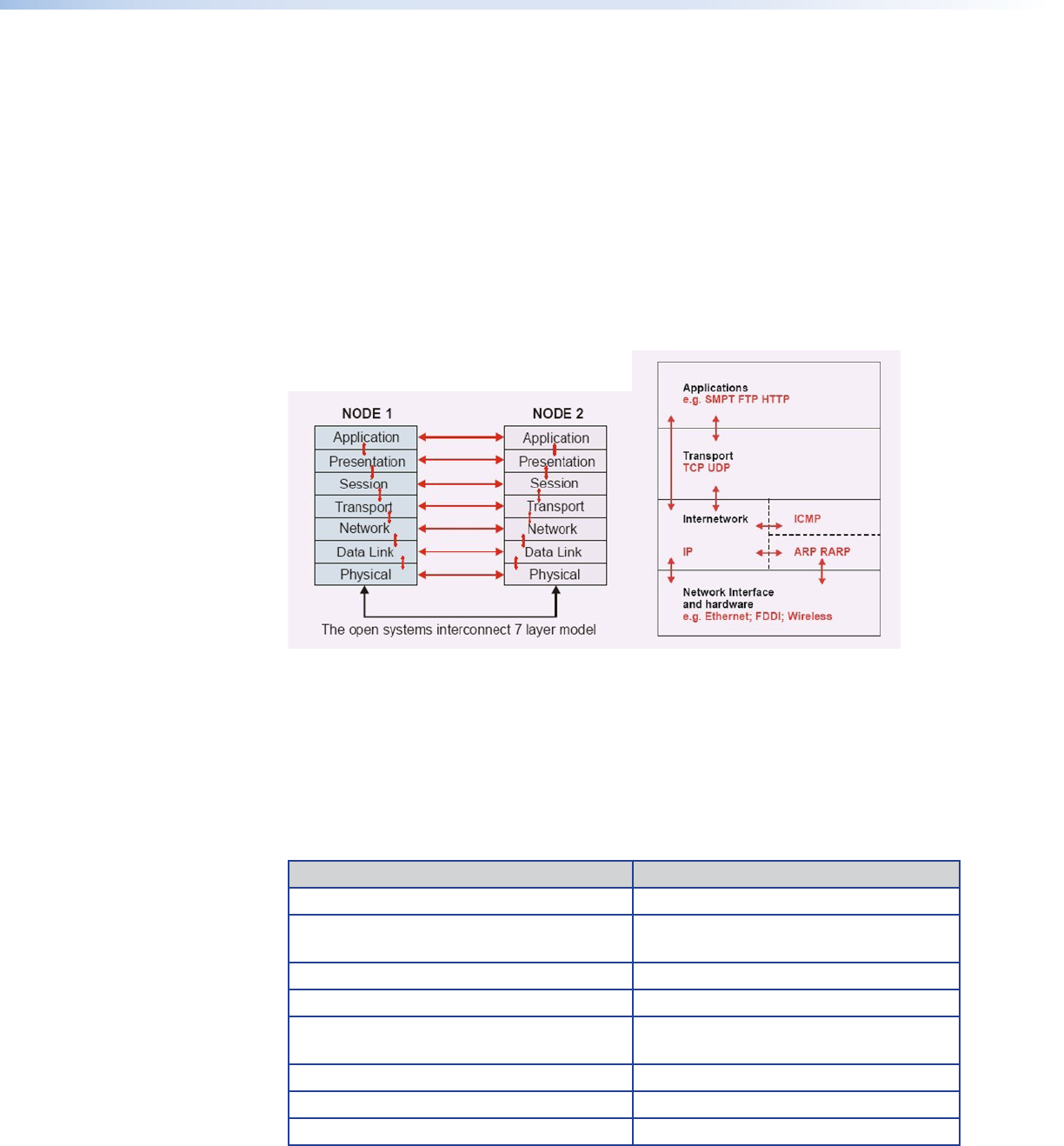
The OSI model is used as a reference, and while some systems follow the full model,
others simplify it by combining the functions of certain layers. In particular the protocol
stack (which is the basis of standard Ethernet communication) only has four layers, as
indicated in the figure below.
The Internetwork layer combines the functions of the Data Link and Network layers of the
OSI model and looks after addressing, carrying Internetwork Protocol (IP) within the MAC
frame. The current version of Internetwork protocol is IPv4 which uses a 32 bit address.
IPv6 with 128 bit addressing is being introduced to solve the possible problem of running
out of available IP addresses and to provide certain other enhancements.
The Transport layer is significant with respect to the transmission of images over networks.
It is here that data is formatted into datagrams suitable for transmission by IP. There are
two significant protocols, User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP).
Figure 54. OSI Model
The OSI model (left) defines seven layers of interconnection. The system behaves as if, at
each layer, there is direct connection between each node; but in fact communication is
through the layers. With Ethernet and most data networks the preferred model is the
TCP/IP four layer protocol stack (right).
Comparison between UDP and TCP
The two different transport layer protocols are compared in the following table:
UDP TCP
Connectionless Connection oriented
Datagrams must be formatted in application Automatically generates datagrams from
bitstream
Multiple applications using ports Multiple applications using ports
Unreliable (best effort) communication Reliable (guaranteed) communication
No flow control (must be in application if
required)
Flow control (deals with out of order data
and error corrections)
No error recovery Error recovery
Multicast possible (one to many) One to one only
Minimum latency Significant latency
VN-Matrix 200 Series • Understanding Network Performance 99