4.1 Control/Sense Commands
C141-C013 201
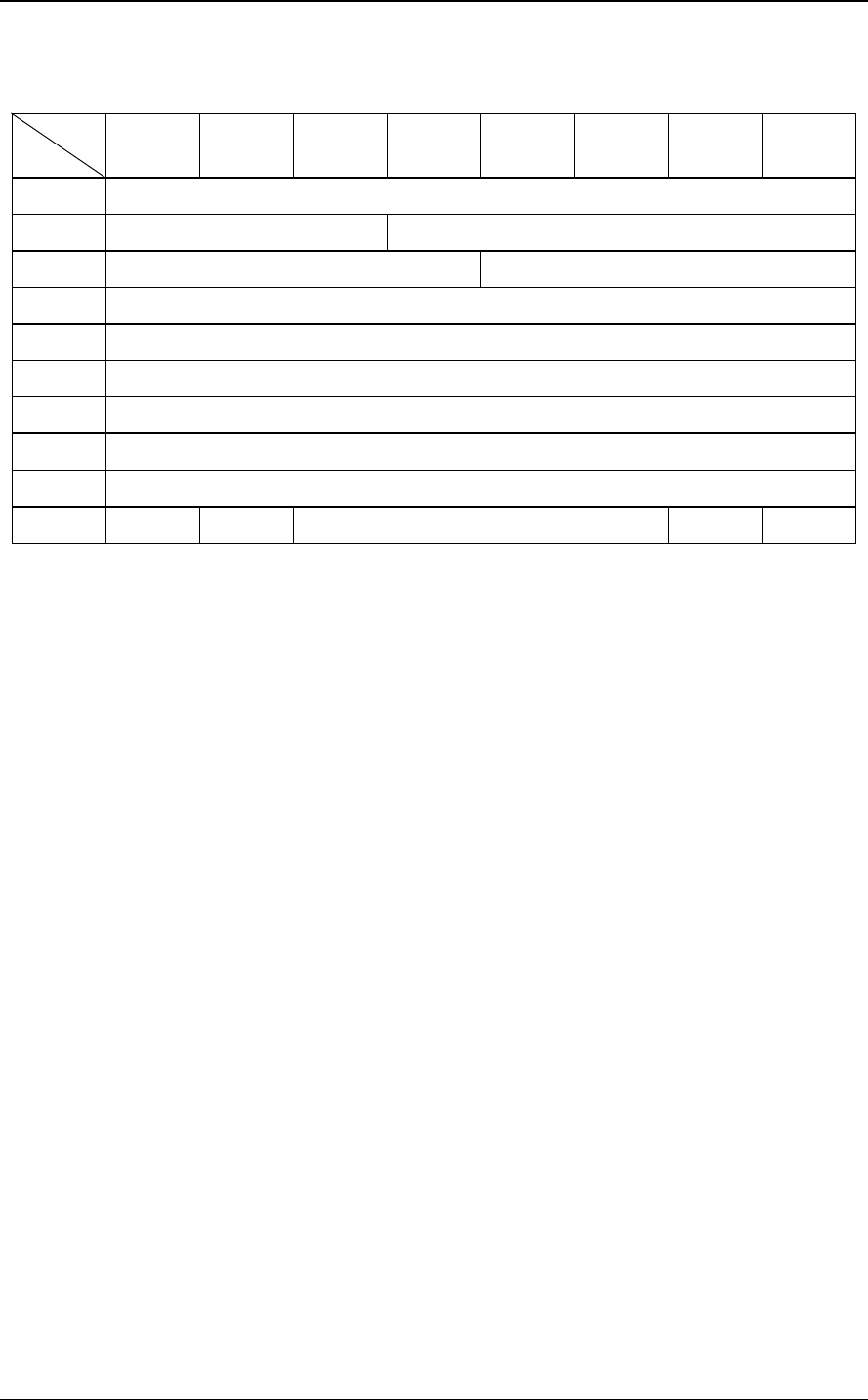
4.1.18 PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT (5F)
Bit
Byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 X'5F'
1 0 0 0 Service Action
2 Scope Type
3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 Parameter List Length (MSB)
8 Parameter List Length (LSB)
9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This command is used for reserving so that the particular initiator can use the
logical unit exclusively or share with others. The command shall be used in
conjunction with the PERSISTENT RESERVE IN command and shall have no
relevance to the RESERVE and RELEASE commands.
By using the reservation key defined by the INIT, PERSISTENT RESERVATION
can be used to identify initiators that execute any of the Service Actions of the
PERSITENT RESERVE OUT commands and that conflict with a reserve
condition established by the RESERVE command. An INIT can check to see
which INITs hold conflicting or illegal reserve conditions by using the
PERSISTENT RESERVE IN command and, if necessary, an INIT can make new
reserve conditions preempt these reserve conditions by using the PERSISTENT
RESERVE OUT command.
Since set reserve conditions cannot be reset by processing such as TARGET
RESET task, PERSISTENT RESERVATION can be used to have multiple INITs
share a device. The PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT and PERSISTENT
RESERVE IN commands provide a fundamental mechanism to analyze reserve
conditions that change dynamically in a multi-initiator system using multi-port
TARGs. It becomes possible to identify whether TARGs have particular reserve
conditions, and to remove reserve conditions from INITs that have errors or are
uncooperative.
If the reserve condition implemented with the RESERVE/RESERVE
EXTENDED command is held when a drive receives this command, this
command is rejected with the report of the RESERVATION CONFLICT status.


















