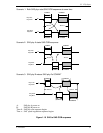
1.3 Phy layer
C141-C013 35
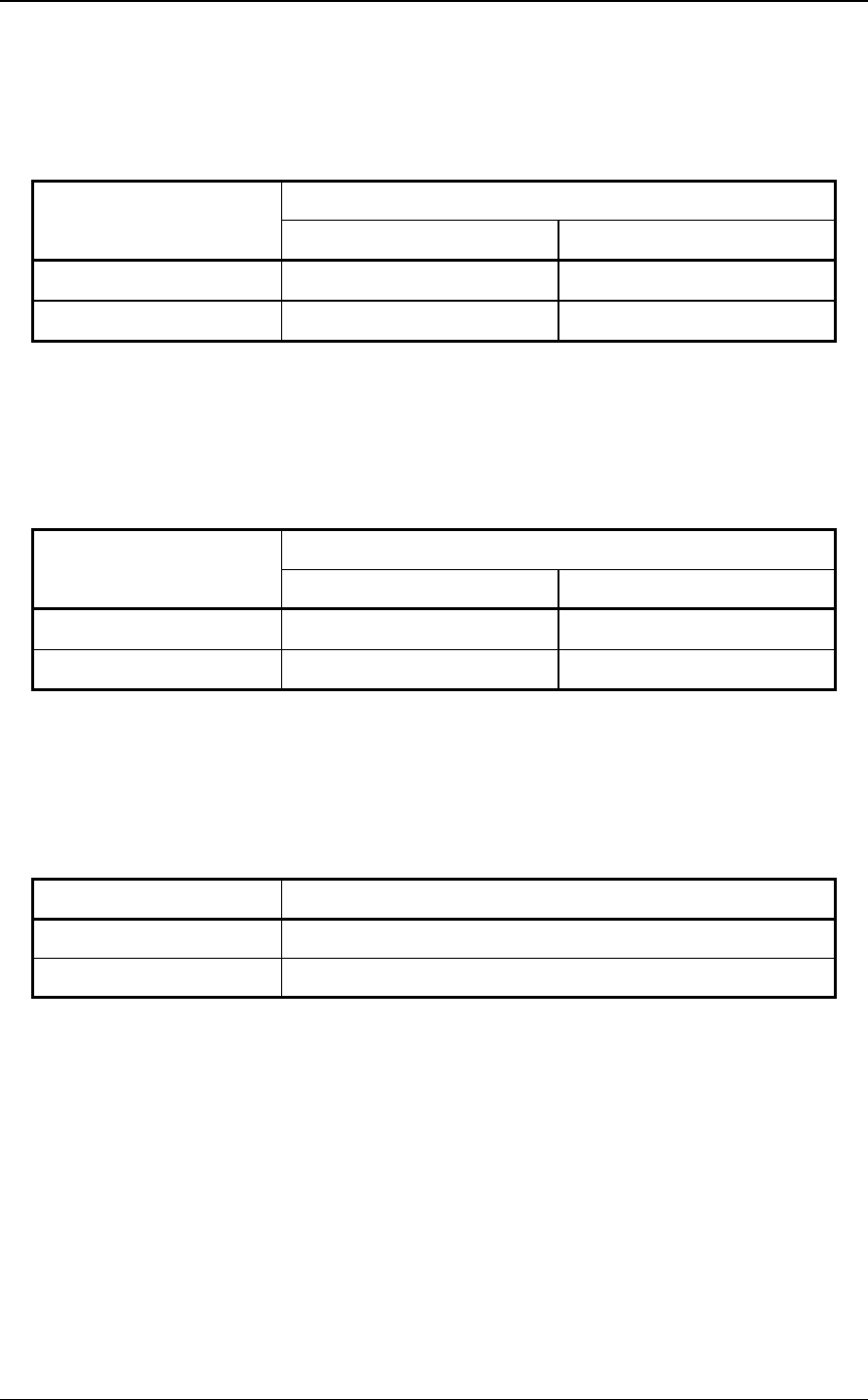
Table 1.6 describes the OOB signal receiver requirements for detecting burst
times, assuming Tburst is the length of the detected burst time. The burst time is
not used to distinguish between signals.
Table 1.6 OOB signal receiver burst time detection requirements
Detection requirements
Signal
may detect shall detect
COMINIT/COMRESET
Tburst ≤ 100 ns
Tburst > 100 ns
COMSAS
Tburst ≤ 100 ns
Tburst > 100 ns
Table 1.7 describes the OOB signal receiver requirements for detecting idle times,
assuming Tidle is the length of the detected idle time.
Table 1.7 OOB signal receiver idle time detection requirements
Detection requirements
Signal
may detect shall detect
COMINIT/COMRESET
175 ns ≤ Tidle < 525 ns 304 ns ≤ Tidle < 336 ns
COMSAS
525 ns ≤ Tidle < 1575 ns 911,7 ns ≤ Tidle < 1008 ns
Table 1.8 describes the OOB signal receiver requirements for detecting negation
times, assuming Tidle is the length of the detected idle time.
Table 1.8 OOB signal receiver negation time detection requirements
Signal Detection requirements
COMINIT/COMRESET Tidle > 525 ns
COMSAS Tidle > 1575 ns
A receiver shall detect an OOB signal after receiving four consecutive idle
time/burst time pairs. It is not an error to receive more than four idle time/burst
time pairs. A receiver shall not detect the same OOB signal again until it has
detected the corresponding negation time (i.e., a COMINIT negation time for a
COMINIT) or has detected a different OOB signal.
A SAS receiver shall detect OOB signals comprised of ALIGNs transmitted at any
rate up to its highest supported physical link rate. This includes physical link rates
below its lowest supported physical link rate (e.g., a SAS receiver supporting only
3,0 Gbps detects 1,5 Gbps based ALIGNs, providing interoperability with a SAS
transmitter supporting both 1,5 Gbps and 3,0 Gbps).