SAS Interface
40 C141-C013
If the phy supports the physical link rate, it shall attempt to synchronize on an
incoming series of dwords at that rate for the SNLT. The received dwords may be
ALIGN (0) or ALIGN (1) primitives. If the phy achieves dword synchronization
within the SNLT, it shall change from transmitting ALIGN (0) primitives to
transmitting ALIGN (1) primitives for the remainder of the SNTT (i.e., the
remainder of the speed negotiation window). If the phy does not achieve dword
synchronization within the SNLT, it shall continue transmitting ALIGN (0)s for
the remainder of the SNTT (i.e., the remainder of the speed negotiation window).
At the end of the SNTT, if a phy is both transmitting and receiving ALIGN (1)
primitives, it shall consider that physical link rate valid. The phy shall then
proceed to the next speed negotiation window. A phy shall participate in all speed
negotiation windows:
a) up to its highest supported physical link rate plus one; or
b) until it runs a speed negotiation window that does not detect a valid physical
link rate after having detected a valid physical link rate in a previous speed
negotiation window.
If the phy has detected a valid physical link rate in the previous speed negotiation
window, it shall enter the final speed negotiation window using the highest
previously successful link rate.
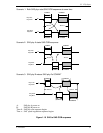
Figure 1.12 shows speed negotiation between a phy A that supports G1 through
G3 link rates and a phy B that only supports the G2 link rate. Both phys run:
1) the G1 speed negotiation window, supported by phy A but not by phy B;
2) the G2 speed negotiation window, supported by both phys; and
3) the G3 speed negotiation window, supported by phy A but not by phy B.
Both phys then select G2 for the final speed negotiation window to establish the
negotiated physical link rate.