6.2 Address Translation
C141-E042-01EN 6-7
6.2 Address Translation
When the IDD receives any command which involves access to the disk medium,
the IDD always implements the address translation from the logical address (a
host-specified address) to the physical address (logical to physical address
translation).
Following subsections explains the CHS translation mode.
6.2.1 Default parameters
In the logical to physical address translation, the logical cylinder, head, and sector
addresses are translated to the physical cylinder, head, and sector addresses based
on the number of heads and the number of sectors per track which are specified
with an INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command. This is called as the
current translation mode.
If the number of heads and the number of sectors are not specified with an
INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command, the default values listed in
Table 6.1 are used. This is called sa the default translation mode. The parameters
in Table 6.1 are called BIOS specification.
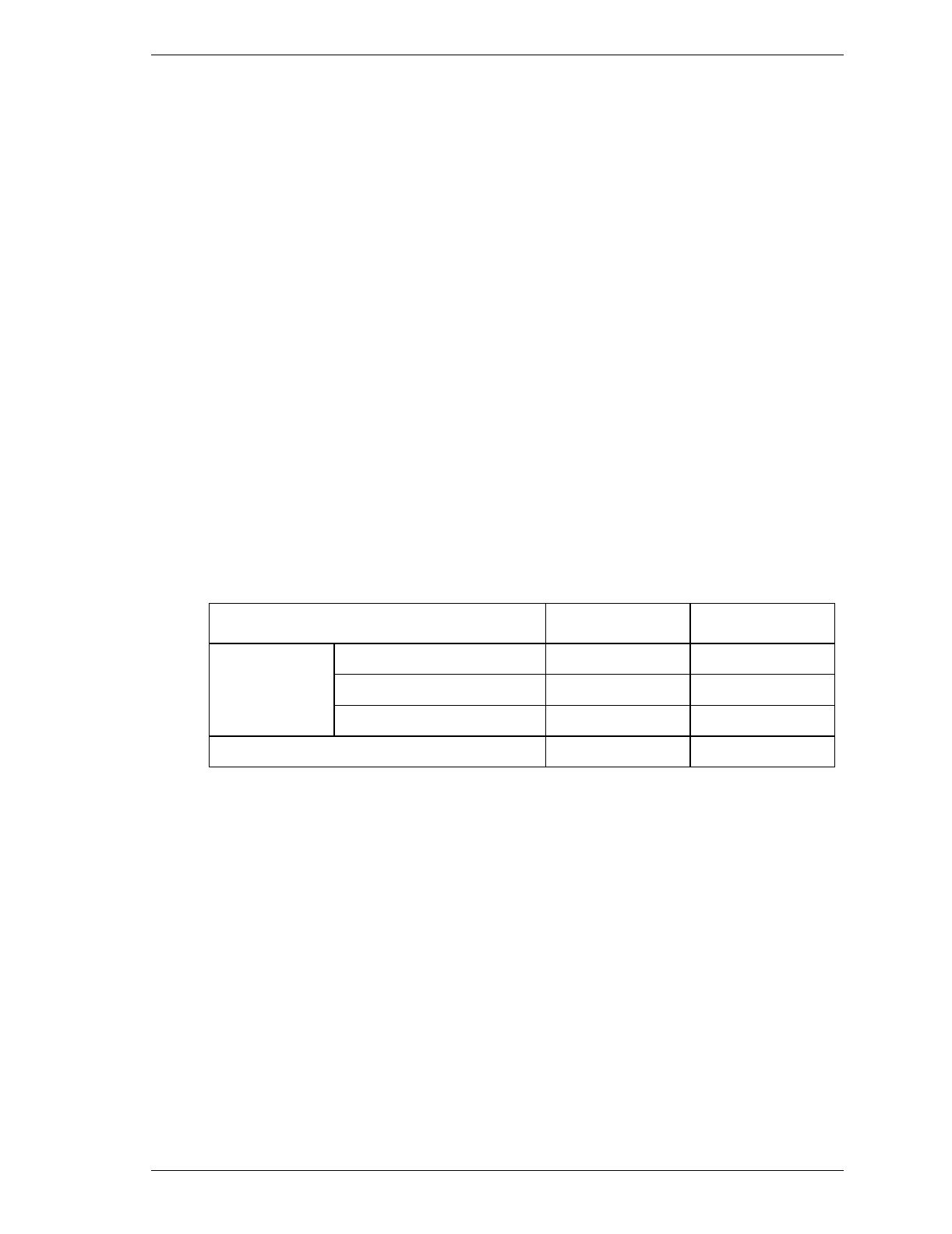
Table 6.1 Default parameters
MHA2021AT MHA2032AT
Number of cylinders 4,200 6,300
Number of heads 16 16
Number of sectors/track 63 63
Formatted capacity (MB) 2,167.6 3,251.4
As long as the formatted capacity of the IDD does not exceed the value shown on
Table 6.1, the host can freely specify the number of cylinders, heads, and sectors
per track.
Generally, the device recognizes the number of heads and sectors per track with
the INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETER command. However, it cannot
recognizes the number of cylinders. In other words, there is no way for the device
to recognize a host access area on logical cylinders. Thus the host should manage
cylinder access to the device.
The host can specify a logical address freely within an area where an address can
be specified (within the specified number of cylinders, heads, and sectors per
track) in the current translation mode.
The host can read an addressable parameter information from the device by the
IDENTIFY DEVICE command (Words 54 to 56).
Parameters
(logical)


















