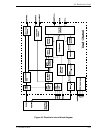
4.7 Servo Control
C141-E042-01EN 4-17
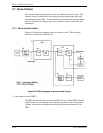
(2) Servo burst capture circuit
The servo burst capture circuit reproduces signals (position signals) that indicate
the head position from the servo data on the data surface. SERVO A, SERVO B,
SERVO C and SERVO D burst signals shown in Figure 4.8 followed the servo
mark, cylinder gray and index information are output from the servo area on the
data surface via the data head. The servo signals A/D-converts the amplitudes of
the POSA, POSB, POSC and POSD signals at the peak hold circuit in the servo
burst capture circuit at the timing of the STROB signal. At that time the AGC
circuit is in hold mode. The difference between A/D-converted data is obtained
in the MPU recognizes it as the position information.
(3) A/D converter (ADC)
The A/D converter (ADC) receives the peak-held servo signals, converts them to
digital, and transfers the digital signal to the DSP unit.
(4) D/A converter (DAC)
The D/A converter (DAC) converts the VCM drive current value (digital value)
calculated by the DSP unit into analog values and transfers them to the power
amplifier.
(5) Power amplifier
The power amplifier feeds currents, corresponding to the DAC output signal
voltage to the VCM.
(6) Spindle motor control circuit
The spindle motor control circuit controls the sensor-less spindle motor. This
circuit detects number of revolution of the motor by the interrupt generated
periodically, compares with the target revolution speed, then flows the current
into the motor coil according to the differentation (abberration).
(7) Driver circuit
The driver circuit is a power amplitude circuit that receives signals from the
spindle motor control circuit and feeds currents to the spindle motor.
(8) VCM current sense resistor (CSR)
This resistor controls current at the power amplifier by converting the VCM
current into voltage and feeding back.