SSL REORGANIZATION clause
U929-J-Z125-9-76 173
Dokuschablonen 19x24 Version 7.3us für FrameMaker V7.x vom 14.02.2007 © cognitas GmbH 2001-2007
24. Oktober 2007 Stand 08:58.55 Pfad: G:\vogt\fsc\uds\Manuale\en\udsent_e\udsent.k05
In case 1), the occupancy level is dependent on the integer specified. It must not fall below
the following value:
integer
Minimum occupancy level [%] = x 100.
integer+1
This means that high occupancy levels are most easily obtained if records are stored in
sorted order. High occupancy levels reduce storage space requirements for tables and
result in shorter access paths.
In order to obtain high occupancy levels by dynamic reorganization, the following must be
taken into consideration:
High values for integer
– are more acceptable for pointer arrays, sort and SEARCH key tables than for lists;
– are more acceptable for records that remain unchanged than for frequently changing
records.
Dynamic reorganization cannot be used for dynamic sets; for multi-level tables it can only
be applied on the lowest table level. Duplicates tables cannot be dynamically reorganized.
The default value for integer is 2.
Examples
DYNAMIC REORGANIZATION SPANS 1 PAGES
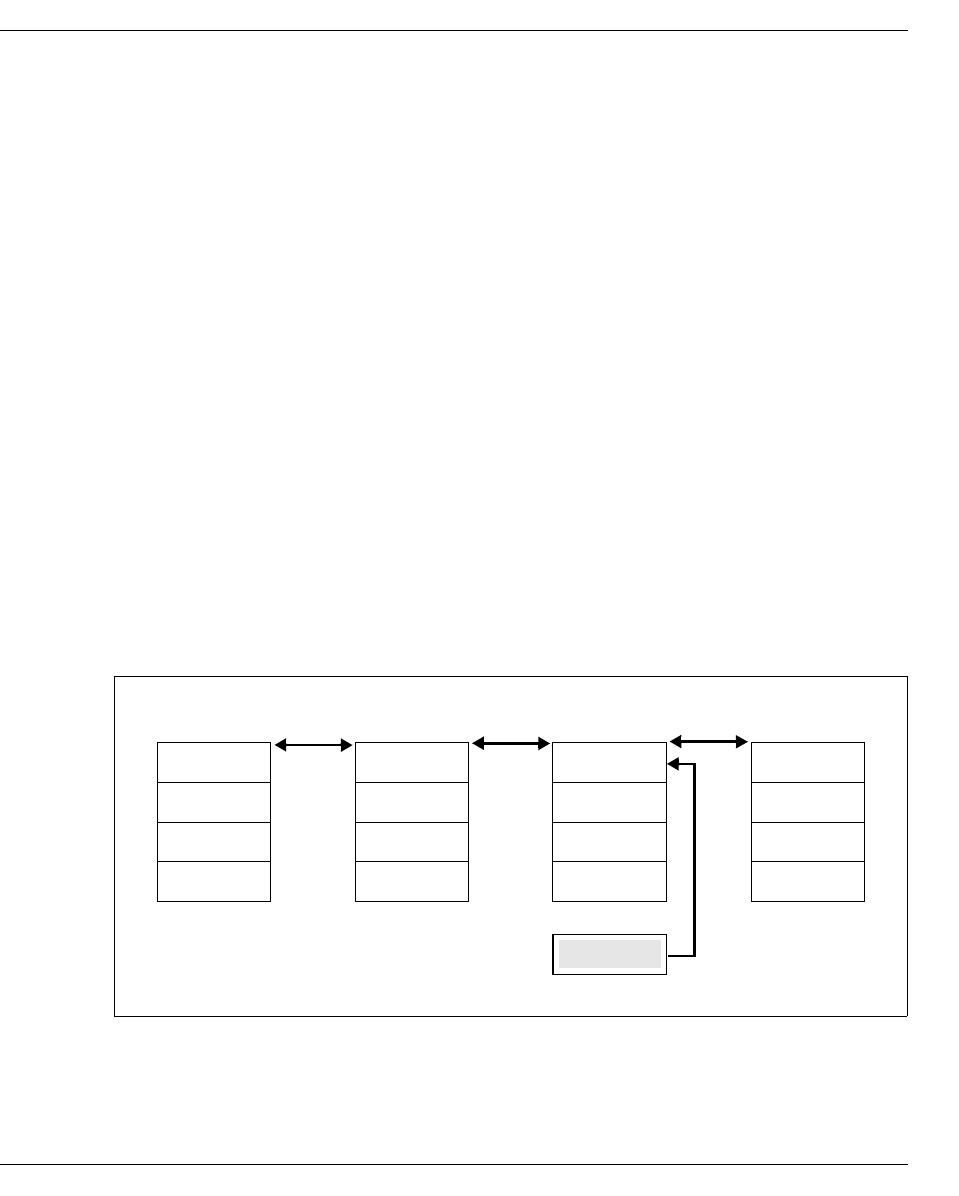
Figure 43: Inserting a record without reorganization
Record 854 can be inserted without reorganization.
Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4
216
470
611
709
715
801
950
1011
854


















