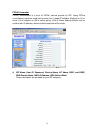
WPA Pre-shared key, One of the biggest drawbacks to traditional WEP security is
that changing the encryption key is optional. Even if you do switch encryption keys
from time to time, there is no option for globally rekeying all access points and all
wireless NICs.
Instead, rekeying is a tedious manual process and is completely impractical for
large organizations. After all, the instant you rekey an access point, none of the
clients will be able to access it until they are also rekeyed.
But with WPA, the rekeying of global encryption keys is required. In the case of
unicast traffic, the encryption key is changed after every frame using Temporary
Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). This protocol allows key changes to occur on a
frame by frame basis and to be automatically synchronized between the access
point and the wireless client. Global rekeying works by advertising the new keys to
wireless clients.
The TKIP is really the heart and soul of WPA security. TKIP replaces WEP
encryption. And although WEP is optional in standard Wi-Fi, TKIP is required in
WPA. The TKIP encryption algorithm is stronger than the one used by WEP but
works by using the same hardware-based calculation mechanisms WEP uses.
The TKIP protocol actually has several functions. First, it determines which
encryption keys will be used and then verifies the client's security configuration.
Second, it is responsible for changing the unicast encryption key for each frame.
Finally, TKIP sets a unique starting key for each authenticated client that is using a
preshared key.
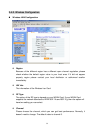
WEP Key
Protects your information with the highest level of industry-standard WEP
encryption: 64/128/152-bit for 802.11b standard, and up to 152-bit for 802.11g
standards. When the “Disable” is selected there is no WEP encryption. When
“64bits”, “128bits” or “152bits” selected there is encrypted date transfer to prevent
unauthorized user to access the wireless network.
There are three levels of encryption 64 bits, 128 bits and 152bits. The 64 bits
encryption is referenced as a lower level encryption. The 152 bits encryption is
referenced as a higher level encryption.
The 64 bits WEP encryption use 40 bits as a secret key, which can controlled by
user, and 24 bits as the initialize vector, which user can not control. These two
portions plus together is 64 bits encryption. Some other vendor’s product might
refer as 40 bits encryption. It is the same thing.
60