Hardware options installation 41
Memory subsystem architecture
The memory subsystem in this server is divided into channels. Each processor supports four channels, and
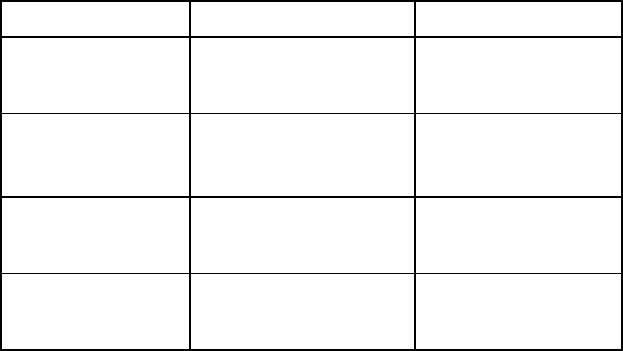
each channel supports three DIMM slots, as shown in the following table.
Channel Population order Slot number
1
A
E
I
12
11
10
2
B
F
J
9
8
7
3
C
G
K
1
2
3
4
D
H
L
4
5
6
For the location of the slot numbers, see "DIMM slot locations (on page 15)."
This multi-channel architecture provides enhanced performance in Advanced ECC mode. This architecture
also enables Lockstep and Online Spare Memory modes.
DIMM slots in this server are identified by number and by letter. Letters identify the population order. Slot
numbers indicate the DIMM slot ID for spare replacement.
Single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs
To understand and configure memory protection modes properly, an understanding of single-, dual-, and
quad-rank DIMMs is helpful. Some DIMM configuration requirements are based on these classifications.
A single-rank DIMM has one set of memory chips that is accessed while writing to or reading from the
memory. A dual-rank DIMM is similar to having two single-rank DIMMs on the same module. A quad-rank
DIMM is, effectively, two dual-rank DIMMs on the same module. The server memory control subsystem selects
the proper rank within the DIMM when writing to or reading from the DIMM.
Dual- and quad-rank DIMMs provide the greatest capacity with the existing memory technology. For
example, if current DRAM technology supports 8-GB single-rank DIMMs, a dual-rank DIMM would be 16
GB, and a quad-rank DIMM would be 32 GB.
LRDIMMs are labeled as quad-rank DIMMs. There are four ranks of DRAM on the DIMM, but the LRDIMM
buffer creates an abstraction that allows the DIMM to appear as a logical dual-rank DIMM to the system. This
is called Rank-Multiplication. The LRDIMM buffer also isolates the electrical loading of the DRAM from the
system to allow for faster operation. These two changes allow the system to support up to three LRDIMMs per
memory channel, providing for up to 50% greater memory capacity and higher memory operating speed
compared to quad-rank RDIMMs.


















