Disaster Tolerance and Recovery in a Serviceguard Cluster
Understanding Types of Disaster Tolerant Clusters
Chapter 1 19
architecture are followed. Extended distance clusters were formerly
known as campus clusters, but that term is not always appropriate
because the supported distances have increased beyond the typical size
of a single corporate campus. The maximum distance between nodes in
an extended distance cluster is set by the limits of the data replication
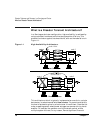
technology and networking limits. An extended distance cluster is shown
in Figure 1-3.
NOTE There are no rules or recommendations on how far the third location
must be from the two main data centers. The third location can be as
close as the room next door with its own power source or can be as far as
in a site across town. The distance among all three locations dictates the
level of disaster tolerance an extended distance cluster can provide.
In an extended distance cluster, for data replication, the Multiple Disk
(MD) driver is used. Using the MD kernel driver, you can configure RAID
1 (mirroring) in your cluster. In a dual data center setup, to configure
RAID 1, one LUN from a storage device in data center 1 is coupled with a
LUN from a storage device in data center 2. As a result, the data that is
written to this MD device is simultaneously written to both devices. A
package that is running on one node in one data center has access data
from both storage devices.
The two recommended configurations for the extended distance cluster
are both described below.