Functional and Operational Characteristics 3-3
Hitachi Universal Storage Platform V/VM User and Reference Guide
Track 32
to
Track 39
Track 32
to
Track 39
Track 40
to
Track 47
Track 56
to
Track 63
Track 48
to
Track 55
Track 48
to
Track 55
Track 40
to
Track 47
Track 56
to
Track 63
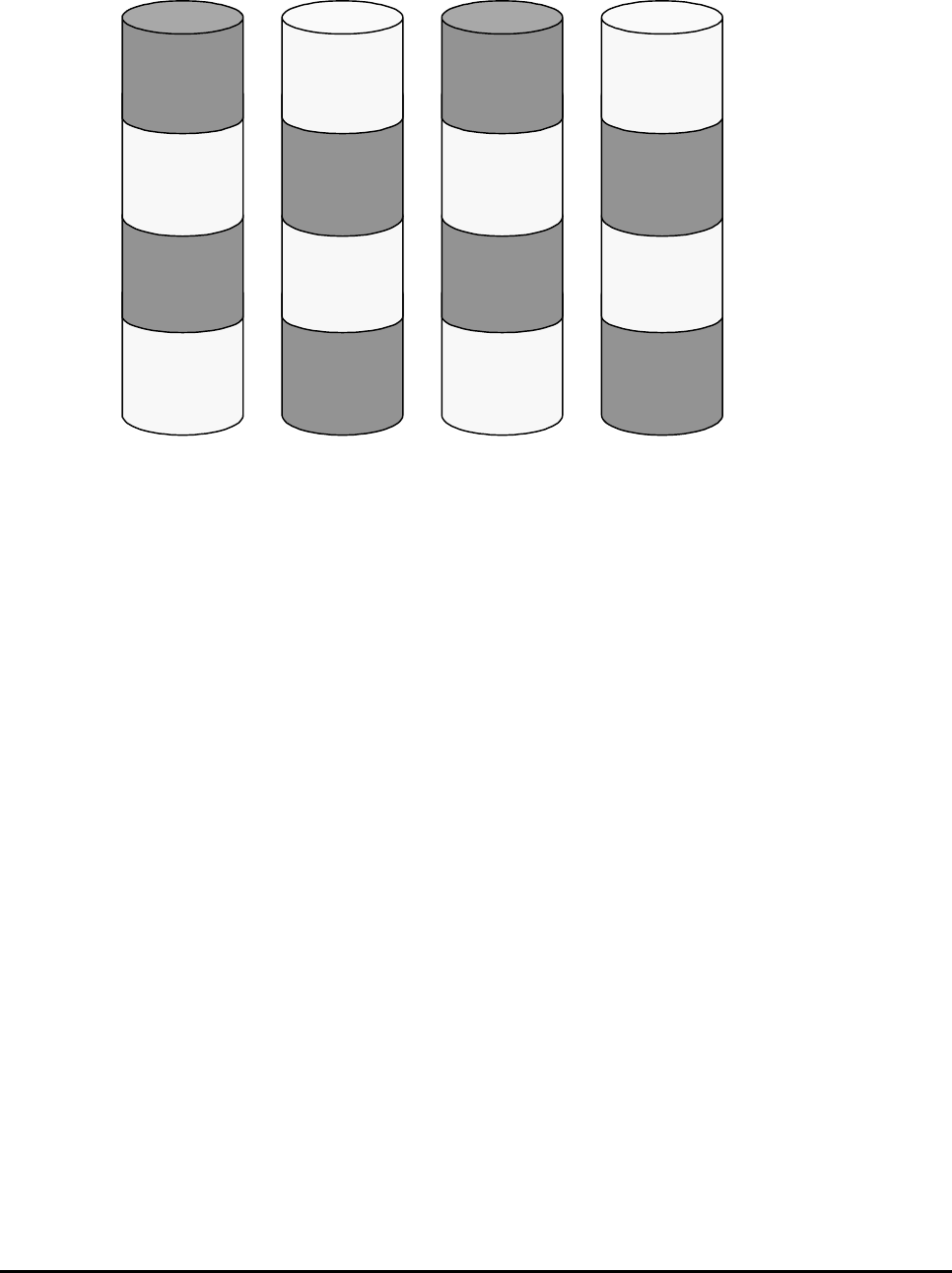
RAID-1 using 2D + 2D and 3390-x LDEVs
Track 0
to
Track 7
Track 0
to
Track 7
Track 8
to
Track 15
Track 24
to
Track 31
Track 16
to
Track 23
Track 16
to
Track 23
Track 8
to
Track 15
Track 24
to
Track 31
Figure 3-1 Sample RAID-1 2D + 2D Layout
RAID-5. A RAID-5 array group consists of four (3D+1P) or eight (7D+1P) disk
drives. The data is written across the four (or eight) disk drives in a stripe that
has three (or seven) data chunks and one parity chunk. Each chunk contains
either eight logical tracks (mainframe) or 768 logical blocks (open). The
enhanced RAID-5+ implementation in the USP V minimizes the write penalty
incurred by standard RAID-5 implementations by keeping write data in cache
until an entire stripe can be built and then writing the entire data stripe to the
disk drives. The 7D+1P RAID-5 increases usable capacity and improves
performance.
Figure 3-2 illustrates RAID-5 data stripes mapped over four physical drives.
Data and parity are striped across each of the disk drives in the array group
(hence the term “parity group”). The logical devices (LDEVs) are evenly
dispersed in the array group, so that the performance of each LDEV within the
array group is the same.
Figure 3-2 also shows the parity chunks that are the
“Exclusive OR” (EOR) of the data chunks. The parity and data chunks rotate
after each stripe. The total data in each stripe is either 24 logical tracks (eight
tracks per chunk) for mainframe data, or 2304 blocks (768 blocks per chunk)
for open-systems data. Each of these array groups can be configured as either
3390-x or OPEN-x logical devices. All LDEVs in the array group must be the
same format (3390-x or OPEN-x). For open systems, each LDEV is mapped to
a SCSI address, so that it has a TID and logical unit number (LUN).


















