Benefits of the SAS Interface 1-7
Copyright © 2006-2007 by LSI Corporation. All rights reserved.
1.5 Benefits of the SAS Interface
SAS is a serial, point-to-point, enterprise-level device interface that
leverages the proven SCSI protocol set. SAS is a convergence of the
advantages of SATA II, SCSI, and fibre channel, and is the future
mainstay of the enterprise and high-end workstation storage markets.
SAS offers a higher bandwidth per pin than parallel SCSI, and improves
signal and data integrity.
The SAS interface uses the proven SCSI command set to ensure reliable
data transfers, while providing the connectivity and flexibility of
point-to-point serial data transfers. The serial transmission of SCSI
commands eliminates clock skew challenges. The SAS interface
provides improved performance, simplified cabling, smaller connectors,
lower pin count, and lower power requirements when compared to
parallel SCSI.
The RAID controller leverages a common electrical and physical
connection interface that is compatible with Serial ATA technology. The
SAS and SATA II protocols use a thin, 7-wire connector instead of the
68-wire SCSI cable or 26-wire ATA cable. The SAS/SATA II connector
and cable are easier to manipulate, allow connections to smaller devices,
and do not inhibit airflow. The point-to-point SATA II architecture
eliminates inherent difficulties created by the legacy ATA master-slave
architecture, while maintaining compatibility with existing ATA firmware.
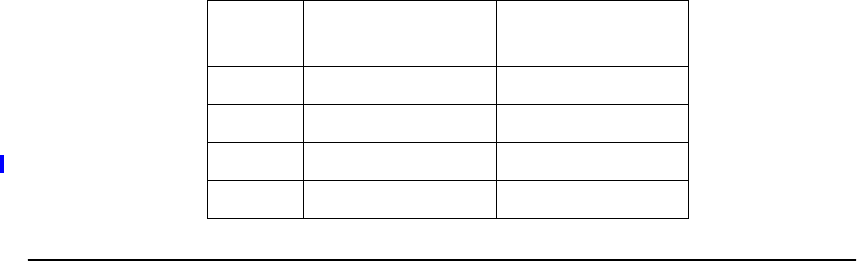
12 2
5 3 32
10 4 16
50 6 32
Table 1.1 Physical Drives Required for Each RAID Level (Cont.)
RAID
Level
Minimum # of
Physical Drives
Maximum # of
Physical Drives


















