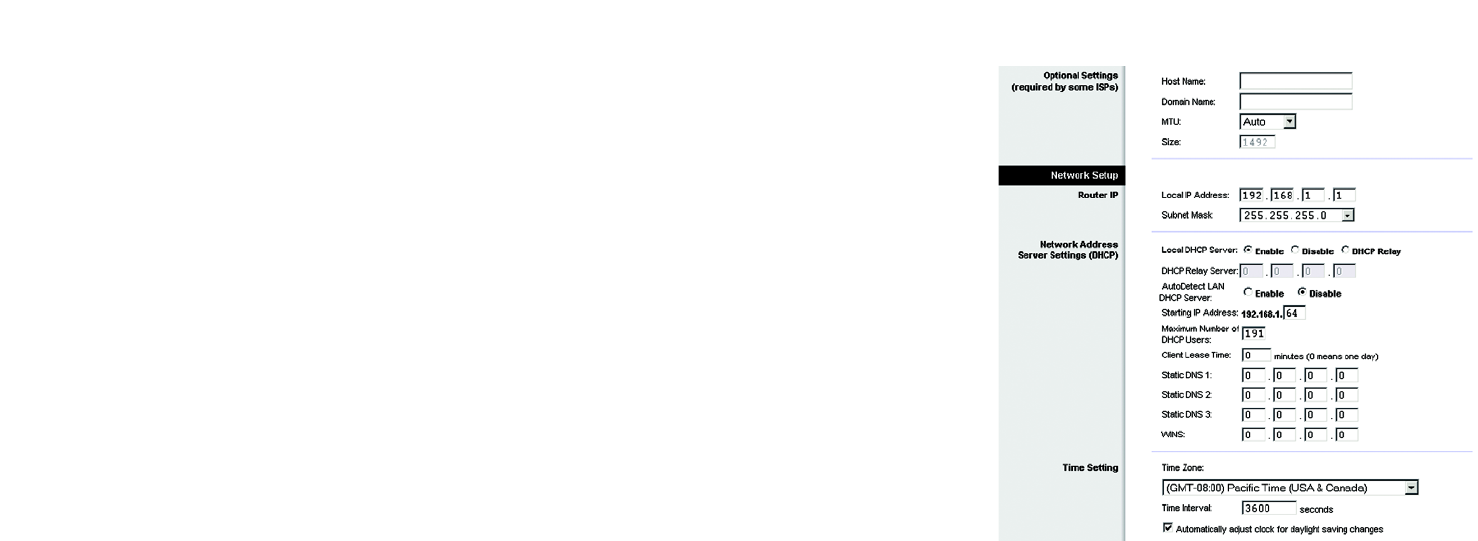
19
Chapter 5: Configuring the Gateway
The Setup Tab
ADSL2 Gateway with 4-Port Switch
Optional Settings (Required by some ISPs)
• Host Name and Domain Name. These fields allow you to supply a host and domain name for the Gateway.
Some ISPs require these names as identification. You may have to check with your ISP to see if your
broadband Internet service has been configured with a host and domain name. In most cases, leaving these
fields blank will work.
• MTU. The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) setting specifies the largest packet size permitted for network
transmission. Select Manual and enter the value desired in the Size field. It is recommended that you leave
this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. By default, MTU is configured automatically.
Network Setup
• Router IP. The values for the Gateway’s Local IP Address and Subnet Mask are shown here. In most cases,
keeping the default values will work.
• Local IP Address. The default value is 192.168.1.1.
• Subnet Mask. The default value is 255.255.255.0.
• Network Address Server Settings (DHCP). A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server automatically
assigns an IP address to each computer on your network for you. Unless you already have one, it is highly
recommended that you leave the Gateway enabled as a DHCP server.
• DHCP Relay Server. If you enable the Local DHCP Server or DHCP Relay for the Local DHCP server, enter
the IP address for the DHCP server in the fields.
• AutoDetect LAN DHCP Server.
• Starting IP Address. Enter a value for the DHCP server to start with when issuing IP addresses. This value
must be 192.168.1. 2 or greater, because the default IP address for the Gateway is 192.168.1.1.
• Maximum Number of DHCP Users. Enter the maximum number of users/clients that can obtain an IP
address. The number will vary depending on the starting IP address entered.
• Client Lease Time. The Client Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed connection
to the Gateway with their current dynamic IP address. Enter the amount of time, in minutes, that the user
will be “leased” this dynamic IP address.
• Static DNS 1-3. The Domain Name System (DNS) is how the Internet translates domain or website names
into Internet addresses or URLs. Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS Server IP Address. You
Figure 5-9: Optional Settings


















