3-22 User’s Reference Guide
In bridge mode the Netopia D-Series performs a simple algorithm. When the Netopia D-Series receives a packet
on the Ethernet hub, the packet is examined for its destination Media Access Control (MAC) address.
The MAC address is the physical address of a device connected to a network, expressed as a 48-bit
hexadecimal number. Sometimes this is called the hardware address, and is a unique number assigned to each
device by the manufacturer.
If the destination MAC address is the Netopia D-Series’s MAC address, based on its serial number, and it is for
management purposes (Telnet or SNMP) or is an ICMP that needs response, it is accepted. If it is the MAC
address that is being proxied (supplied by the DSLAM) it is encapsulated in ATM FUNI and transmitted over the
DSL connection. A packet received from the DSL connection will be de-encapsulated and its MAC address
examined. Either it is management traffic for the Netopia D-Series, or it is encapsulated for Ethernet and
transmitted over the hub.
DD
DD
SS
SS
UU
UU
mm
mm
oo
oo
dd
dd
ee
ee
The DSU behavior is similar, except that the datalink encapsulation on the WAN is Frame Relay, and the
destination for packets from the WAN is the Auxiliary port. The Ethernet hub is only available for management
(Telnet or SNMP).
A special male HD-15 to female V.35 cable supports the Netopia D-Series as a DCE connecting the Auxiliary
port to a Frame Relay Access Device (FRAD) such as a sync serial router.
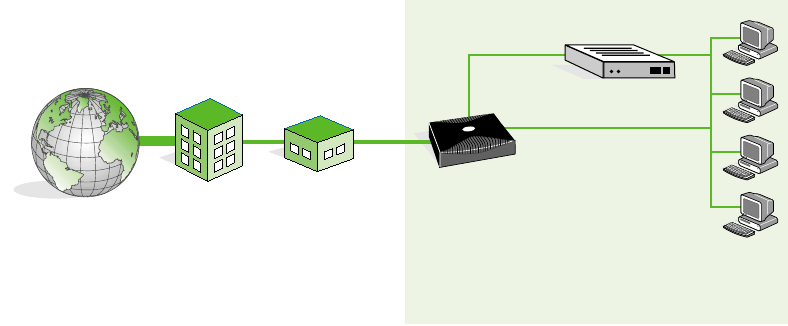
The following figure shows a typical configuration for the DSU mode:
The sections that follow refer to the filtering bridge mode only.
ISP
Servers or
Workstations
BUSINESS
T
H
E
I
N
T
E
R
N
E
T
Netopia D
7
100
SDSL CSU/DSU
Router
SDSL
Ethernet (management)
V.
35
CENTRAL
OFFICE