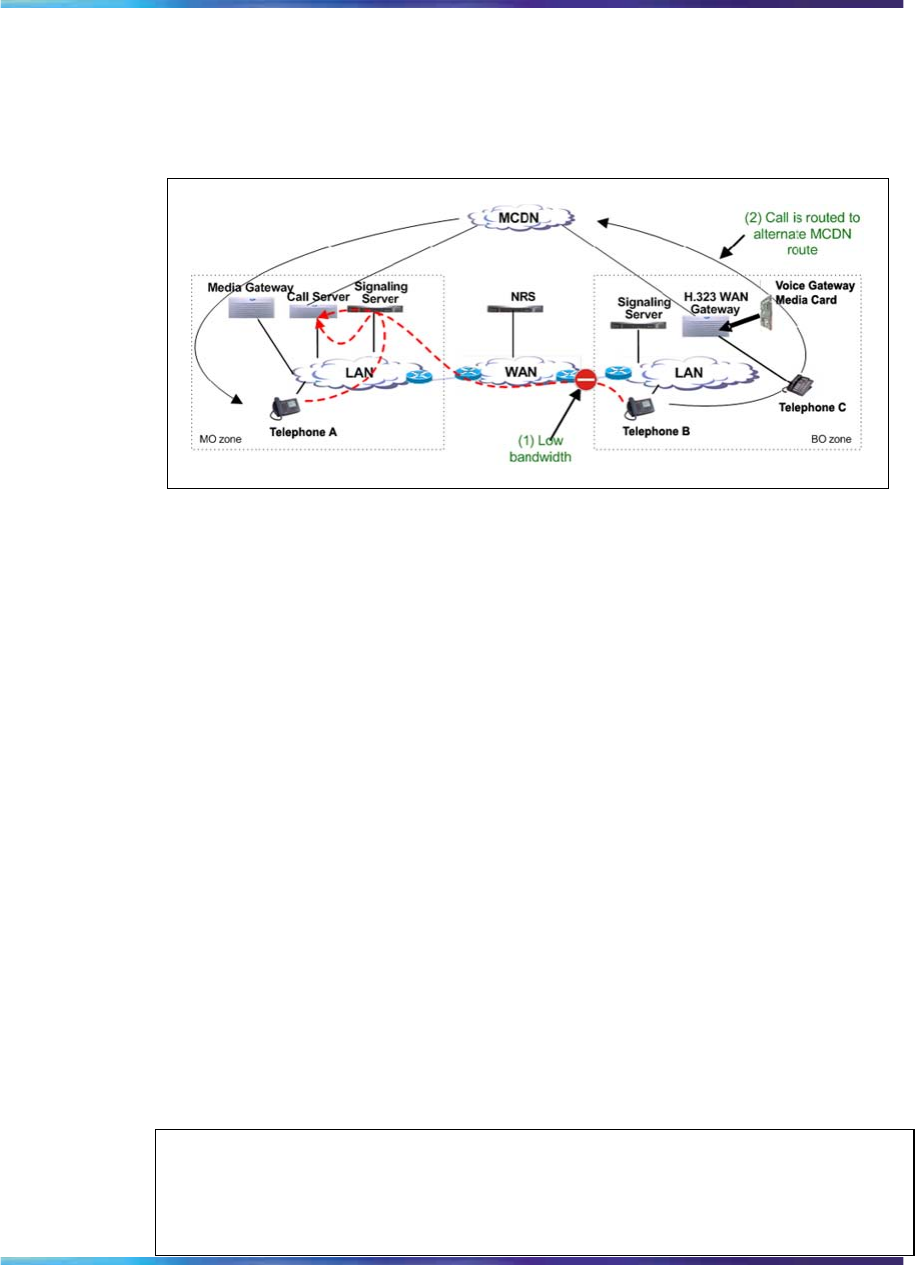
160 Alternative Call Routing for Network Bandwidth Management
Event number 1 pertains to the originally dialed call that experiences low
bandwidth or unacceptable QoS conditions. Event number 2 pertains to
the alternately routed call.
Figure 65
Example of Alternative Call Routing for NBWM in operation
There are multiple choices of alternate routes provided for the overflowed
calls. Network administrators who do not want calls to be blocked, but
have a limited amount of bandwidth available, want to overflow calls
to conventional trunks, (Public Switched Telephone Network [PSTN] or
TIE/Meridian Customer Defined Network [MCDN]). This feature allows
calls to be routed by overflowing them, trading off the capital cost of WAN
bandwidth against the incremental cost of overflowed calls.
Nortel recommends that this feature be used with DID (Direct Inward Dial)
numbers. This allows calls that are rerouted over the PSTN to ring the
intended telephone directly. It is possible to use this feature without having
DID, so that when the call gets rerouted over the PSTN the call reaches an
attendant console or a specific telephone.
When there is insufficient bandwidth for a station-to-station call, the
Alternative Call Routing for NBWM feature uses a trunk for a call which
would not normally use a trunk.
Prior to the introduction of the Alternative Call Routing for NBWM feature,
there was no alternate routing mechanism for the following types of
station-to-station calls:
•
Branch office calls to or from the main office
•
Branch office calls to or from another branch office controlled by the
same main office
ATTENTION
The term branch office refers to Media Gateway 1000B (MG 1000B) and
Survivable Remote Gateway (SRG) systems in this document.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Main Office Configuration Guide for SRG 50
NN43001-307 02.02 Standard
Release 5.0 3 December 2007
Copyright © 2005-2007, Nortel Networks
.


















