D100.05
15
D100
Bit
14 13 12 11 10 9876543210
E0_100.03
D200.00D100.05
W0.00
TIM
100-ms timer (BCD)
100-ms timer (binary)
Timer number
Timer number
Set value
Set value
0001
#10
W0.01
TIMX(550)
0002
#01FF
The BCD TIM and binary TIMX instructions can be used together.
D100 [W100]
Offset n (number of words)
Starting word address
Starting word address: D100
Offset +n
CH 15 0
Array Variable: ABC
Example
Ladder language:
Copy ABC[3] to D200
ST language:
Substitute ABC[0] to ABC[3].
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
WORD data
MOV
ABC[3]
D200
5.00
To access
this data,
specify ABC
[3].
14
More Flexible Programming
The Greatest Program Diversity in the industry. A programming environment has been created that is highly
readable and can flexibly support changes in specifications, to enable efficient design and program entry
with few mistakes.
Highly Readable Programming
Programs are easy to see and easy to understand.
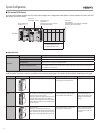
Bit Addresses can be used in the DM Area and EM Area.
DM and EM Area bits could not be specified with the previous
SYSMAC PLCs, but they can with the CJ2 CPU Units.
Examples
D100.05: Bit 05 of D100
E0_100.05: Bit 03 of E0_100
NEW
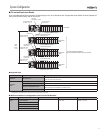
BCD and Binary Timer Instructions can be used Together.
With the CJ1 CPU Units, it was necessary to select in the initial setup of the CPU Unit whether BCD or binary
was to be used as the data format for timer instructions. With the CJ2 CPU Units, BCD or binary can be
selected individually for each instruction by setting the data format of the timer set value.
NEW
Address Offsets can be Specified
An offset can be specified in brackets after a starting
address to offset the starting address. If an address
in I/O memory is specified as the offset, the final
address can be dynamically specified according to
the contents of the specified memory address.
Example
D100[W100]: D100 is the starting address and the contents of W100
is the offset. If W100 is &5, then D105 is specified.
NEW
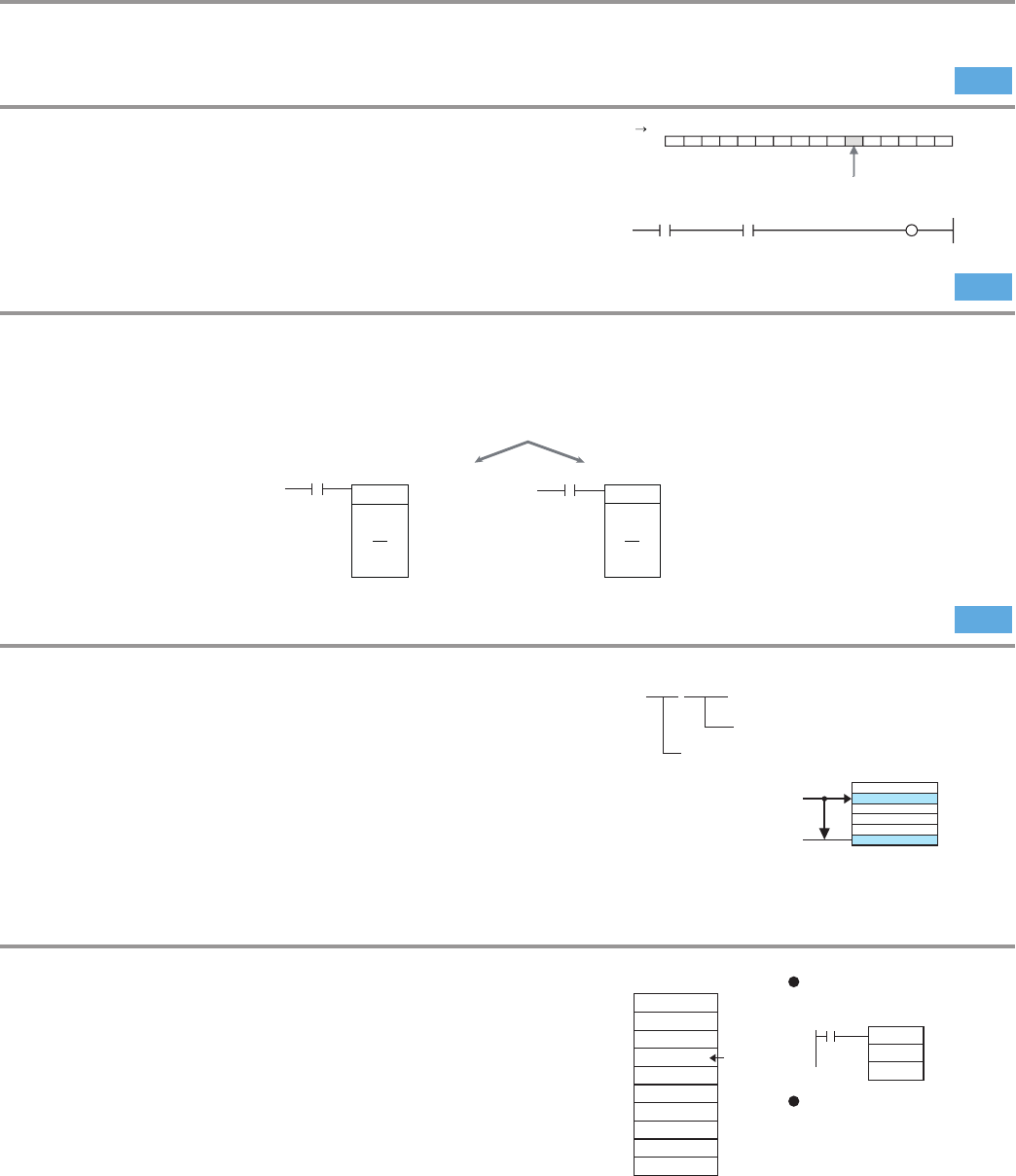
Array Variables make Data Specification Easier to Understand.
By using array variables, any data in a string of
data can be expressed using a subscript, making
programming easy to understand. Array variables
can also be used for data stacks and function block
I/O variables. Because they can be set for network
symbols, the exchange of multiple data items
with external devices can be easily programmed.
(Usable languages: Ladder, ST, SFC).