10
11.2.0
Slave Port Functionality
11.2.1
Modbus Communications
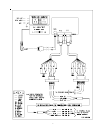
The T-3 Modbus Slave card runs the RTU version of the Modbus protocol. This capability
allows the module to communicate data from a Raypak B6000 Boiler Control to a Modbus
Master host, and vice-versa. The module supports both point-to-point implementation as
well as multi-drop implementations.
The following discusses the functional capabilities of the T-3 card.
11.2.1.1 Command/Reply Cycle
Successful communications between the card and a host will always con-
sist of the following two transactions:
Command: Message from master giving instruction to slave.
Reply: Response to command.
A slave station will respond to a master issued command in several ways.
Data Message: If the command was executed by the T-3 board, the re-
sponse message will include the data requested, or an acknowledge-
ment that the command was executed.
Error Message: If the command could not be executed by the T-3
board, for whatever reason, an error response message is transmitted to
the master. The error response message consists of the original function
code (ORed with 80hex) and error code.
No Reply: If the master does not detect a reply within its time-out pe-
riod, the master should retransmit the command, before a time out error is
issued. If the Slave could not decode the message or an error occurred
preventing the Slave from recognizing the message, no response will be
issued.
11.2.1.2 Command Types
The T-3 can respond to three types of commands from the master;
read data, write data, and a diagnostic command. These are overviewed
below:
Read Data: The following type of data read commands are supported:
2 Read Input Status
3 Read Multiple Registers
4 Read Input Registers
Write Data: The Following data write command is supported:
6 Single Register Write
Diagnostics: The diagnostic command is supported:
8 Loopback test - Code 0
11.2.1.3 Command Error Checking
When the T-3 cannot execute a command, an error code is generated and
returned to the master. Error codes generated at the slave will usually be
indicative of an illegal function, an illegal address, bad data, or the inability
to complete a transaction because of a network problem.