User Manual
Publication date: March, 2007
Revision A1
41
There are many types of VLAN applied. Most popular is port-based VLAN,
tag-based VLAN and protocol-based VLAN.
Port-based VLAN
Some physical ports are configured as members of a VLAN. All stations
attached on these ports can communicate with each other.
Tag-based VLAN
It identifies the membership by VLAN ID, no matter where the packet
comes from. It is also referred to as 802.1Q VLAN.
Protocol-based VLAN
It identifies the VLAN membership by layer 3 protocol types, for example
IPX, Appletalk, IP, etc.
Other VLAN technologies not mentioned above are MAC-based VLAN, IP-
based VLAN and so on.
Terminology
Tagged Frame:
A frame, carrying a tag field following the source MAC address, is four bytes
long and contains VLAN protocol ID and tag control information composed of user
priority, Canonical Format Indicator (CFI) and optional VLAN identifier (VID).
Normally, the maximal length of a tagged frame is 1522 bytes.
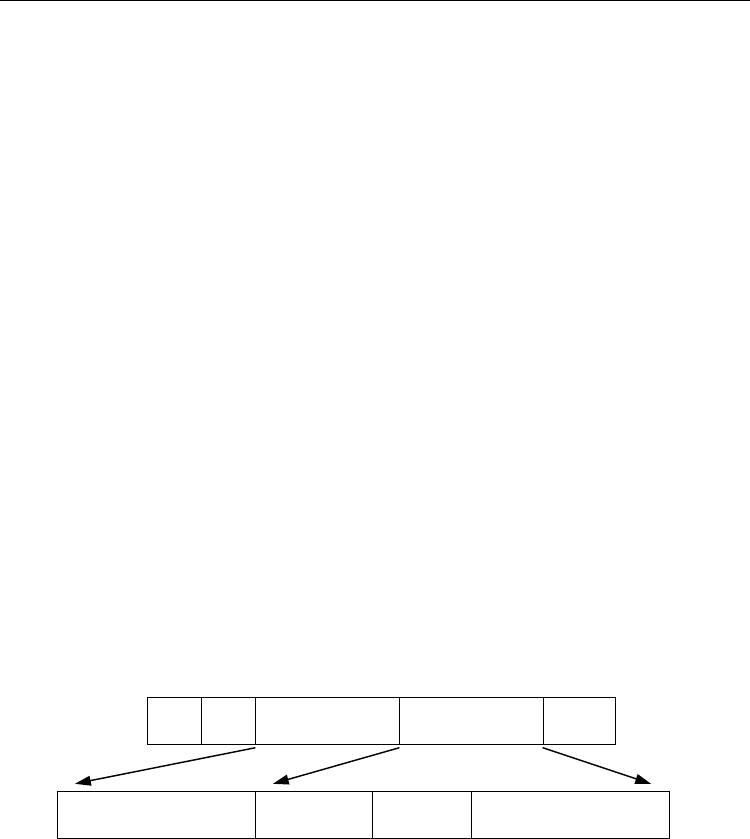
802.1Q VLAN-tagged Ethernet frame
6 6 2 2 2
DA SA
VLAN Protocol
ID
Tag Control
Information
Length
/Type
VLAN Protocol ID =
0x8100
User Priority CFI VLAN identifier
Fig.3-9 Tag Format
VLAN Protocol ID: 8100 is reserved for VLAN-tagged frame.
User Priority: 3 bits long. User priority is defined to 7 – 0. 0 is the lowest
priority.
CFI: Canonical Format Indicator. 1 bit long. It is used to encapsulate a
token ring packet to let it travel across the Ethernet. Usually, it is
set to 0.
VLAN ID: 12 bits long. 0 means no VLAN ID is present. 1 means default VLAN,
4095 reserved.


















