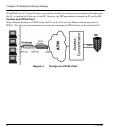
Prestige 310 Broadband Sharing Gateway
Glossary
L
Glossary of Terms
Bandwidth This is the capacity on a link usually measured in bits-per-second (bps).
Bit (Binary Digit) -- A single digit number in base-2, in other words, either a 1 or a zero.
The smallest unit of computerized data.
Broadband Broadband refers to telecommunication that provides multiple channels of data over a
single communications medium.
Byte A set of bits that represent a single character. There are 8 bits in a Byte.
CDR Call Detail Record. This is a name used by telephone companies for call related
information.
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol is an alternative protocol to PAP. It
avoids sending passwords over the wire by using a challenge/response technique.
Client A software program that is used to contact and obtain data from a Server software
program on another computer. Each Client program is designed to work with one or
more specific kinds of Server programs, and each Server requires a specific kind of
Client. A Web Browser is a specific kind of Client.
Crossover Ethernet
cable
A cable that wires a pin to its opposite pin, for example, RX+ is wired to TX+. This
cable connects two similar devices, for example, two data terminal equipment (DTE) or
data communications equipment (DCE) devices.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol automatically assigns IP addresses to clients
when they log on. DHCP centralizes IP address management on central computers
that run the DHCP server program. DHCP leases addresses for a period of time which
means that addresses are made available to assign to other systems.
DNS Domain Name System. A database of domain names and their IP addresses. DNS is
the primary naming system for many distributed networks, including the Internet.
Domain Name The unique name that identifies an Internet site. Domain Names always have 2 or
more parts, separated by dots. The part on the left is the most specific, and the part on
the right is the most general.
DSL/xDSL Digital Subscriber Line technologies enhances the data capacity of the existing twisted-
pair wire that runs between the local telephone company switching offices and most
homes and offices. There are actually seven types of DSL service, ranging in speeds
from 16 Kbits/sec to 52 Mbits/sec. The services are either symmetrical (traffic flows at
the same speed in both directions), or asymmetrical (the downstream capacity is
higher than the upstream capacity). DSL connections are point-to-point dedicated
circuits, meaning that they are always connected. There is no dial-up. There is also no
switching, which means that the line is a direct connection into the carrier’s frame