5
Glossary of Terms – continued
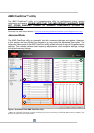
CPU / CPU NB Voltage OFFSET: Most AMD “Scorpius” platform technology motherboards have a BIOS option
that allows Voltage adjustments beyond the CPU VID Voltage range. This voltage offset is added on top of the
VID value. Voltage offset could be negative or positive. Actual voltage level = CPU or CPU NB VID + OFFSET.
Example: VID 1.350V + 0.100V OFFSET = 1.450V actual voltage level.
One of the following options will be available in the BIOS menu (depending on motherboard model):
• “CPU Voltage” and “CPU NB Voltage” item that includes both VID and OFFSET values merged into one
voltage adjustment item (the range can go to over 2.0V)
• Separate items for CPU VID and CPU Voltage – here the “CPU Voltage” value starts from the VID
value and then adds Offset on top of the VID
• CPU and CPU NB “OFFSET” items that control the amount of Voltage offset
In all cases the voltage level can be tuned on the fly with AMD OverDrive utility (VID sliders). Please monitor the
actual voltage level via the Hardware Monitoring.
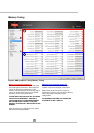
CPU / CPU NB Voltage OVERRIDE: Some AMD “Scorpius” platform technology motherboards (such as the
ASUS Crosshair 5) have a BIOS option that allows the motherboard to override the CPU VID value requested
by the CPU by directly programming the voltage regulator. In this case the CPU Core Voltage and/or CPU NB
Voltage will remain at a fixed voltage level. The motherboard BIOS may call this option as “manual voltage
mode”. VID Override (or VID Bypass) may allow voltage levels that exceed the range of CPU VID values. In the
case of AMD FX-8150 the VID range enables voltages of up to 1.550V – VID OVERRIDE may allow over 2.0V.
Note: If VID OVERRIDE / Bypass has been activated the CPU VID value adjustments via AMD OverDrive (or
other software) will no longer have any impact on the actual voltage level. The only way to adjust the voltage is
by directly programming the voltage regulator. The motherboard vendor may provide a software for this
purpose.
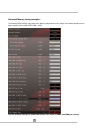
AMD Turbo Core Technology: AMD Turbo Core Technology and Application Power Management (APM) allow
the CPU cores to run above the CPU Base clock value as long as the CPU remains within the thermal and
power limits. As an example the AMD FX-8150 CPU has a base clock of 3600MHz but it can run at 3900MHz
when up to 8 cores are active and at 4200MHz when up to 4 cores are active assuming it stays within the power
and thermal limits. Under very heavy workloads the CPU will return to the base clock – 3600MHz in the case of
AMD FX-8150 CPU.
Since APM sets a predefined TDP limit it is usually recommended to disable both AMD Turbo Core Technology
and APM features when increasing the CPU frequency and voltage above the default levels. The AMD Turbo
Core Technology and APM can be disabled via AMD OverDrive utility or from the motherboard BIOS menu.