Metered Rack PDU User Guide49
Environment
Configure Temperature and Humidity Sensors
Path: Environment
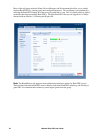
Through the Environment tab, when you have a temperature or a temperature and humidity sensor
connected to the Rack PDU, you can set thresholds for Warning and Critical alarm generation (see
“Device status icons” on page 42 for details on each type of alarm).
For temperature:
• If the high temperature threshold is reached, the system generates a Warning alarm.
• If the maximum temperature threshold is reached, the system generates a Critical alarm.
Similarly, for humidity:
• If the low humidity threshold is reached, the system generates a Warning alarm.
• If the minimum humidity threshold is reached, the system generates a Critical alarm.
Note: Click the thermometer symbol in the upper right corner to toggle between Fahrenheit and
Celsius.
To configure temperature and humidity sensors:
1. Enter values for minimum, maximum, high, and low thresholds.
2. Enter Hysteresis values. (See “Hysteresis” on page 49 for details.)
3. Enable alarm generation as desired.
4. Click Apply.
Hysteresis. This value specifies how far past a threshold the temperature or humidity must return to
clear a threshold violation.
• For Maximum and High temperature threshold violations, the clearing point is the threshold
minus the hysteresis.
• For Minimum and Low humidity threshold violations, the clearing point is the threshold plus the
hysteresis.
Increase the value for Temperature Hysteresis or Humidity Hysteresis to avoid multiple alarms if
temperature or humidity that has caused a violation then wavers slightly up and down. If the hysteresis
value is too low, such wavering can cause and clear a threshold violation repeatedly.
Example of rising but wavering temperature: The maximum temperature threshold is 85°F, and the
temperature hysteresis is 3°F. The temperature rises above 85°F, violating the threshold. It then wavers
down to 84°F and then up to 86°F repeatedly, but no clearing event and no new violation occur. For the
existing violation to clear, the temperature would have to drop to 82°F (3°F below the threshold).
Example of falling but wavering humidity: The minimum humidity threshold is 18%, and the humidity
hysteresis is 8%. The humidity falls below 18%, violating the threshold. It then wavers up to 24% and
down to 13% repeatedly, but no clearing event and no new violation occur. For the existing violation to
clear, the humidity would have to rise to above 26% (8% past the threshold).