30
ATM VC
ATM settings are used to connect to your ISP. Your ISP provides VPI, VCI settings to you. In
this Device, you can totally setup 8 VCs on different encapsulations, if you apply 8 different
virtual circuits from your ISP. You need to activate the VC to take effect. For PVCs
management, you can use ATM QoS to setup each PVC traffic line's priority.
Virtual Circuit: VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) and VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier) define a
virtual circuit.
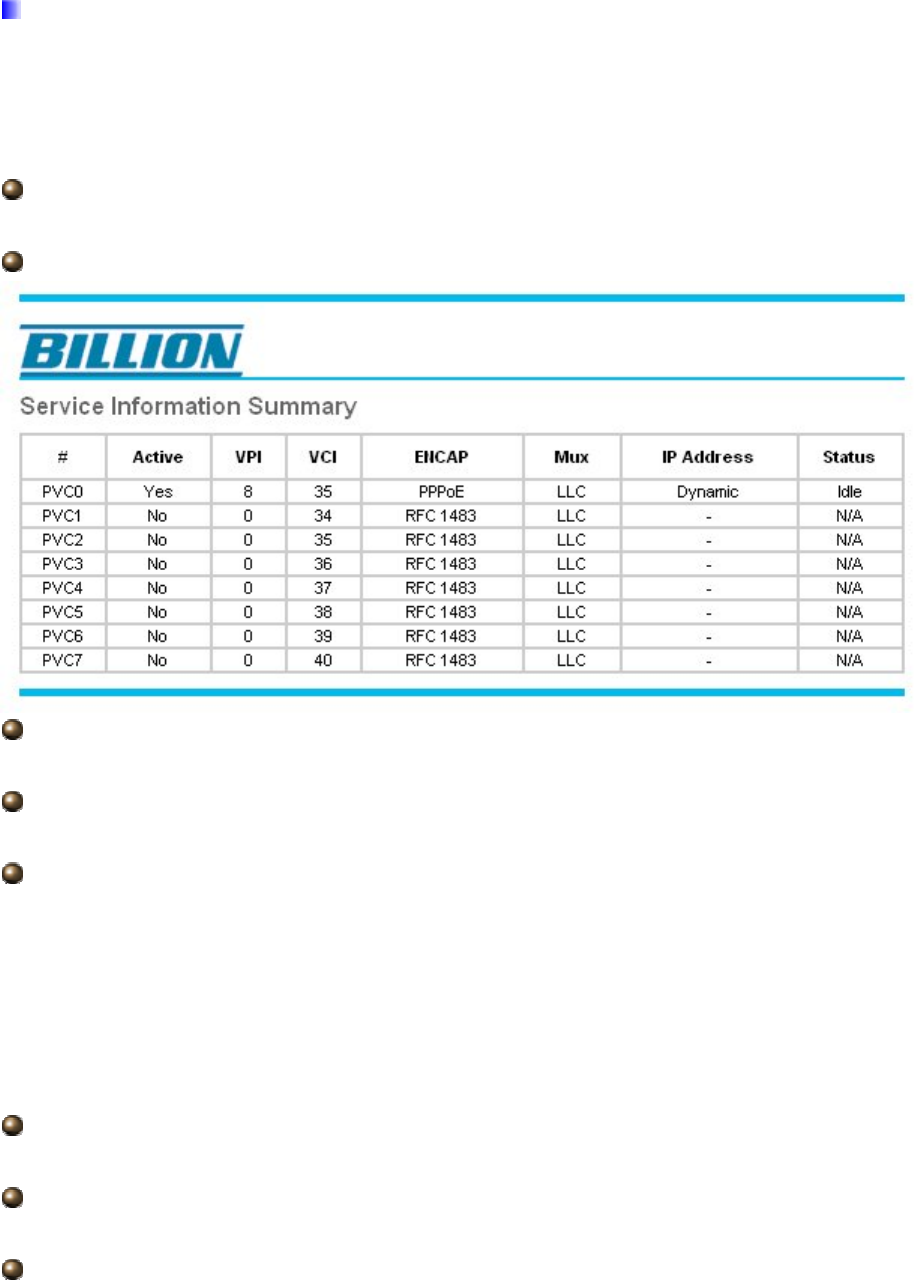
PVC Summary:
VPI: The valid range for the VPI is 0 to 255. Enter the VPI assigned to you. This field may
already be configured.
VCI: The valid range for the VCI is 1 to 65535. Enter the VCI assigned to you. This field
may already be configured.
ATM QoS: Select the Quality of Service types for this Virtual Circuit. The ATM QoS types
include CBR (Constant Bit Rate), VBR (Variable Bit Rate) and UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate).
These QoS types are all controlled by the parameters specified below, including PCR, SCR
and MBS.
Select CBR to specify fixed (always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR for
applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR for burst traffic and
bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak Cell
Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
MBS: Maximum Burst Size (MBS) refers to the maximum number of cells that can be sent
at the peak rate. Type the MBS, which is less than 65535