34
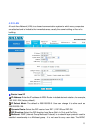
5200N supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP-v2. Select None to disable it
IGMP Snoop: Choose Disabled or Enabled IGMP Snoop function.
DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual
clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server.
DHCP:
If set to Enabled, your BiPAC 5200N can assign IP addresses, an IP default gateway and
DNS servers to Windows 95, Windows NT and other systems that support the DHCP client.
If set to Disabled, the DHCP server will be disabled.
If set to Relay, the BiPAC 5200N acts as a surrogate DHCP server and relays DHCP
requests and responses between the remote server and the clients. Enter the IP address of
the actual, remote DHCP server in the Remote DHCP Server field in this case.
When DHCP is used, the following items need to be set.
Starting IP Address: This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP
address pool.
IP Pool Count: This field specifies the size or count of the IP address pool.
Lease Time: The current lease time of client.
Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers. The DNS servers are
passed to the DHCP clients along with the IP address and the subnet mask.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers. The DNS servers
are passed to the DHCP clients along with the IP address and the subnet mask.
4.2.3 Wireless
This section introduces the wireless LAN and some basic configurations. Wireless LANs can
be as simple as two computers with wireless LAN cards communicating in a peer-to-peer
network or as complex as a number of computers with wireless LAN cards communicating
through access points which bridge network traffic to the wired LAN.