Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide
Cisco SWAN Framework Overview
8
Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide
OL-6217-01
The Cisco SWAN framework introduces WLCCP to facilitate control messaging between the framework
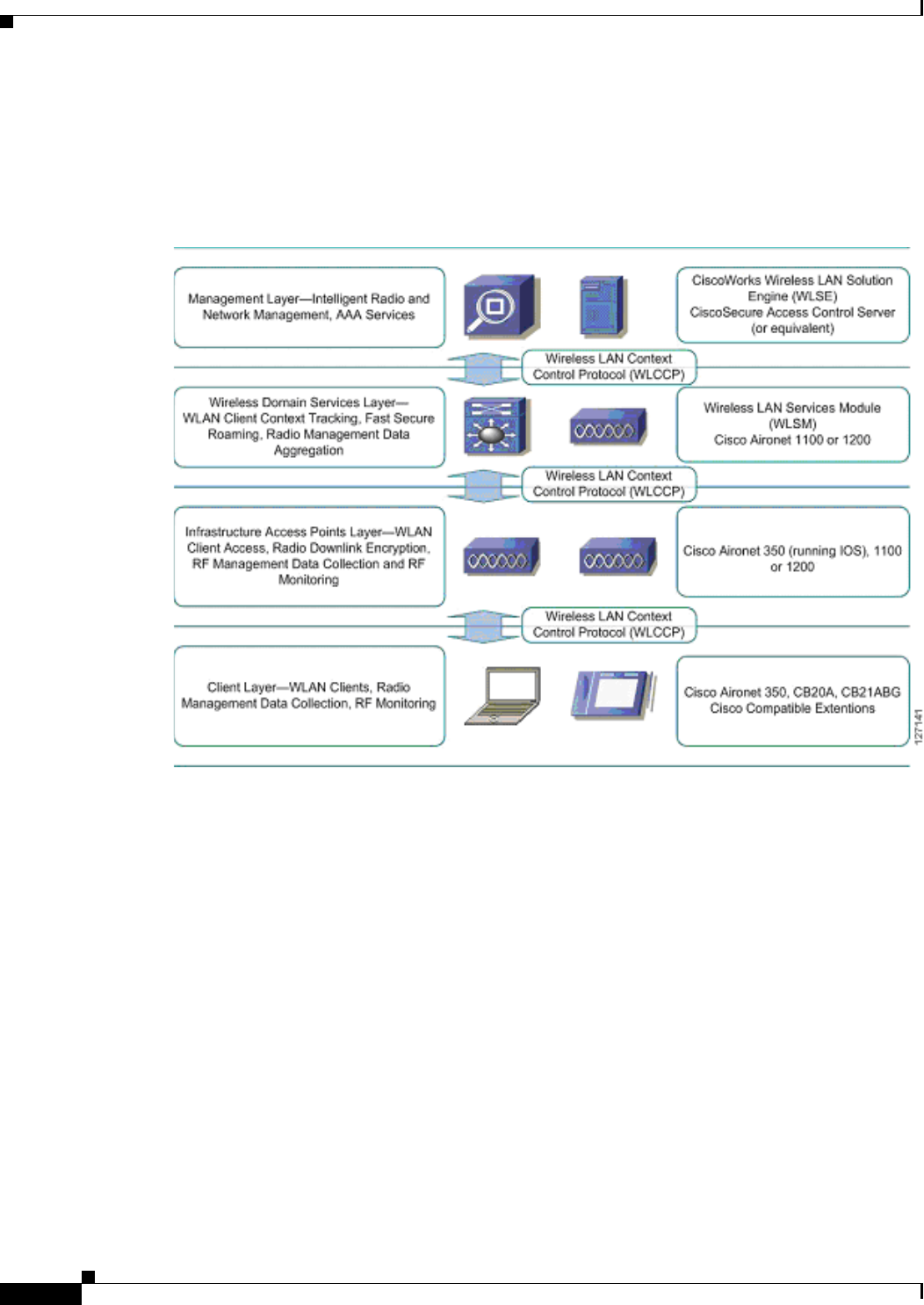
components. Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual model of the Cisco SWAN framework, including the
WLCCP messaging protocol. As shown in Figure 1, each layer is implemented in specific Cisco
products.
Figure 1 Cisco SWAN Layers
The management layer supplies the processing of RM data from the lower layers, controlling and
managing the radio coverage environment. This data is also used for securing the radio coverage
environment by detecting rogue access points and wireless clients. Authentication, Authorization, and
Accounting (AAA) services are also placed in the management layer.
The required management layer component is the CiscoWorks WLSE. An optional component is the
CiscoSecure ACS. Other products with functionality equivalent to ACS may be used in Cisco SWAN.
The WDS layer provides critical services: WLAN client context awareness, fast secure roaming, and
aggregation of radio management data from the infrastructure access point and client layer. WDS is
implemented in supporting versions of Cisco IOS for the Cisco Aironet 1100 and 1200 series access
points and on the special Cisco IOS running on the wireless LAN service module for the Catalyst 6500
switch platform. The solution architecture dictates whether to use the WDS access point or the WLSM
implementation.
The infrastructure access point layer facilitates WLAN client access to the wired-network, radio
downlink encryption, and radio management data collection, including on-going radio monitoring.
The client layer includes all wireless clients. Advanced SWAN framework features take advantage of
client-side capabilities to allow for radio measurement collection from the WLAN clients and fast secure
roaming.


















