Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide
Cisco SWAN Framework Overview
9
Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide
OL-6217-01
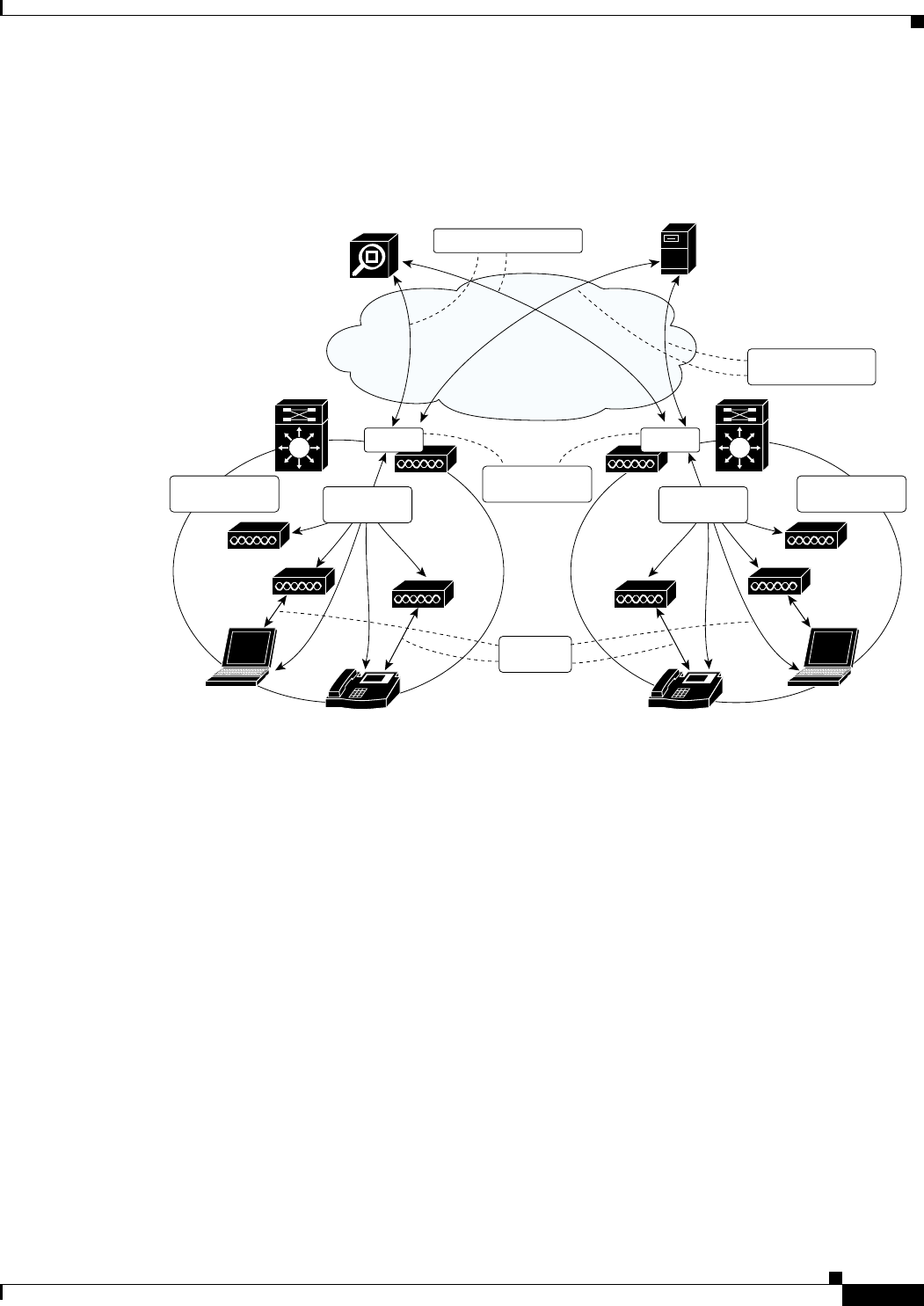
Figure 2 represents a logical, hierarchical view of the SWAN framework that clearly illustrates the
importance of the WDS layer.
Figure 2 Cisco SWAN Logical View
WDS are configured to run on a supporting device—either a Cisco Aironet 1100 or 1200 for a Layer 2
architectural solution or the WLSM for an switch-based, Layer 3 solution. In both cases, infrastructure
access points register with the WDS using special WLCCP messages.
Once registered, the infrastructure access points forward client association, authentication, and roaming
information through the WDS via WLCCP MN registration messages, allowing the WDS to control and
track wireless clients. If client authentication is implemented via any 802.1x with EAP (such as Cisco
LEAP, EAP-FAST, PEAP, EAP-TLS, or EAP-TTLS), the WDS performs an additional important role by
acting as the 802.1x authenticator for all wireless clients. In 802.1x authentication transactions, the WDS
communicates directly with the RADIUS server. Any valid wireless client associated with an
infrastructure access point and registered with the WDS.
A WDS, its registered infrastructure access points, and registered clients make up a WLAN control
domain. Wireless clients can seamlessly roam between access points within a WLAN control domain. A
WDS also collects radio management data from the infrastructure access points and, potentially, the
MNs within the WLAN control domain via special WLCCP radio management (WLCCP-RM)
messages. This data is aggregated by the WDS and passed on to the WLSE in WLCCP-RM messages.
The WLSE uses this RM data to control and manage the radio coverage environment and to detect rogue
access points and clients.
Cisco SWAN offers two basic WLAN architectures: an architecture supporting a Layer 2 WLAN control
domain and an architecture supporting a Layer 3 WLAN control domain. The Layer 2 architecture
leverages access point-based WDS. This architecture is called the access point-based WDS solution. The
Layer 3 architecture leverages WLSM-based WDS and is called the switch-based WDS solution.
IP IP
WLCCP messages
127430
802.1x
authenticator
WDS
WLSE
ACS
WDS
WLCCP
messages
WLCCP
messages
WLAN control
domain
WLAN control
domain
Data
packets
RADIUS control
domain


















