Wireless-G Broadband Router with 2 Phone Ports
43
Chapter 5: Configuring the Router
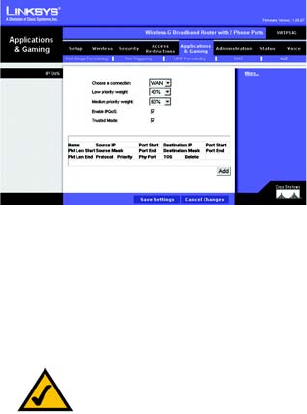
The Applications & Gaming Tab - QoS
The Applications & Gaming Tab - QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) ensures better service to high-priority types of network traffic, which may involve
demanding, real-time applications, such as Internet phone calls or videoconferencing.
Use this screen to configure IP QoS for connections, view the rules you have set up, and manage your rules.
IP QoS
Choose a connection. Choose the appropriate connection from the drop-down menu.
Low priority weight. Select the weight of the low priority queue, which is available in increments of 10%. The
sum of the low and medium priority weights should equal 100%.
Medium priority weight. Select the weight of the medium priority queue, which is available in increments of
10%. The sum of the low and medium priority weights should equal 100%.
Enable IP QoS. Click this checkbox to enable IP QoS for the selected connection.
Trusted Mode. The Router has two modes for management of queue traffic. Click the Trusted Mode checkbox if
you want the Router to apply all of the IP QoS rules first, regardless of the TOS bit settings. After the rules have
been applied, then the TOS bit settings will be applied. If Trusted Mode is not used, then the Router will use the
un-trusted mode. The default rule will be applied if the there is no match between the un-trusted mode and the
rules of the Trusted Mode. (The default rule will assign a low queuing priority.)
The following table will list the rules you have configured. You can also add new rules and delete existing rules.
Each rule uses the criteria you specified to identify specific types of application traffic, which should be assigned
to one of the Router’s three priority queues: High, Medium, or Low.
Figure 5-28: Applications & Gaming Tab -
QoS
NOTE: If IP QoS is enabled and
you have no defined rules, then
a default rule will be
implemented. All traffic will be
transmitted in the Low priority
queue.


















