56
Key Length – You can choose “64-bit” to use WEP with 64-bit key length encryption or choose “128-
bit” to use WEP with 128-bit key length encryption. The longer key length can provide better
security but worse transmission throughput.
Key Format – You may select to use ASCII Characters (alphanumeric format) or Hexadecimal digits
(in the "A-F", "a-f" and "0-9" range) to be the WEP Key.
PassPhrase – A passphrase simplifies the WEP encryption process by automatically generating the
WEP encryption keys for the print server.
Default Key – Select one of the four keys to encrypt your data. Only the key you select it in the
“Default key” will take effect.
Key 1 – Key 4 – The WEP keys are used to encrypt data transmitted within the wireless network. Fill
the text box by following the rules below:
64-bit WEP: Input 10-digit Hex values (in the "A-F", "a-f" and "0-9" range) or 5-digit ASCII
character as the encryption keys. For example: “0123456aef“ or “Guest“.
128-bit WEP: Input 26-digit Hex values (in the "A-F", "a-f" and "0-9" range) or 10-digit ASCII
characters as the encryption keys. For example:
“01234567890123456789abcdef“ or “administrator“.
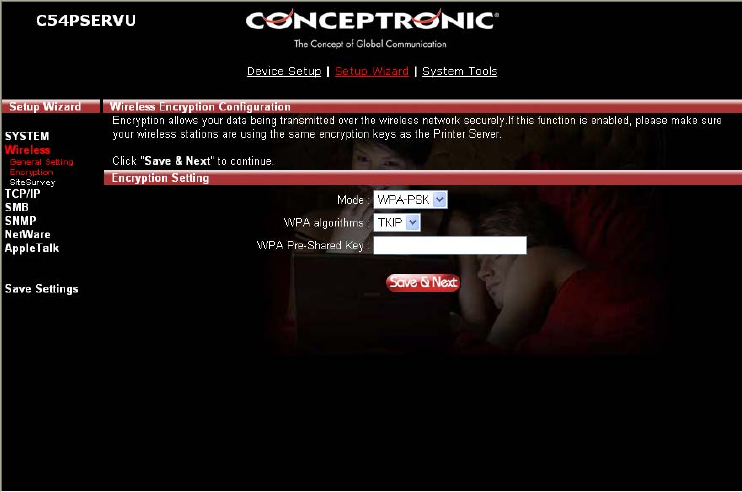
WPA-PSK Security Mode:
When “WPA-PSK”, also named “WPA-shared key” requires users to select the advanced encryption
methods, i.e. TKIP and enter a set of shared key.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the temporal key every 10,000 packets. This
insures much greater security than the standard WEP security.
WPA Key – Enter 8 to 63 digits of ASCII format to be the key for the authentication within the
network.
When you finish configuring the wireless security, click “Save & Next” to confirm the configuration.