PRELIMINARY
CY14B101P
Document #: 001-44109 Rev. *B Page 9 of 32
Write Protection and Block Protection
CY14B101P provides features for both software and hardware
write protection using WRDI instruction and WP
. Additionally, this
device also provides block protection mechanism through BP0
and BP1 pins of the Status Register.
The write enable and disable status of the device is indicated by
WEN bit of the status register. The write instructions (WRSR,
WRITE, and WRTC) and nvSRAM special instruction (STORE,
RECALL, ASENB, ASDISB) need the write to be enabled (WEN
bit = 1) before they can be issued.
Write Enable (WREN) Instruction
On power up, the device is always in the write disable state. The
following WRITE, WRSR, WRTC, or nvSRAM special instruction
must therefore be preceded by a Write Enable instruction. If the
device is not write enabled (WEN = ‘0’), it ignores the write
instructions and returns to the standby state when CS
is brought
HIGH. A new CS
falling edge is required to re-initiate serial
communication. The instruction is issued following the falling
edge of CS. When this instruction is used, the WEN bit of status
register is set to ‘1’.
Note After completion of a write instruction (WRSR, WRITE, or
WRTC) or nvSRAM special instruction (STORE, RECALL,
ASENB, ASDISB) instruction, WEN bit is cleared to ‘0’. This is
done to provide protection from any inadvertent writes.
Therefore, WREN instruction needs to be used before a new
write instruction can be issued.
Write Disable (WRDI) Instruction
Write Disable instruction disables the write by clearing the WEN
bit to ‘0’ in order to protect the device against inadvertent writes.
This instruction is issued following the falling edge of CS
followed
by opcode for WRDI instruction. The WEN bit is cleared on the
rising edge of CS
following a WRDI instruction.
Block Protection
Block protection is provided using the BP0 and BP1 pins of the
Status register. These bits can be set using WRSR instruction
and probed using the RDSR instruction. The nvSRAM is divided
into four array segments. One-quarter, one-half, or all of the
memory segments can be protected. Any data within the
protected segment is read only. Table 5 shows the function of
Block Protect bits.
Hardware Write Protection (WP Pin)
The write protect pin (WP) is used to provide hardware write
protection. WP
pin allows all normal read and write operations
when held HIGH. When the WP
pin is brought LOW and WPEN
bit is “1”, all write operations to the status register are inhibited.
The hardware write protection function is blocked when the
WPEN bit is “0”. This allows the user to install the CY14B101P
in a system with the WP
pin tied to ground, and still write to the
status register.
WP
pin can be used along with WPEN and Block Protect bits
(BP1 and BP0) of the status register to inhibit writes to memory.
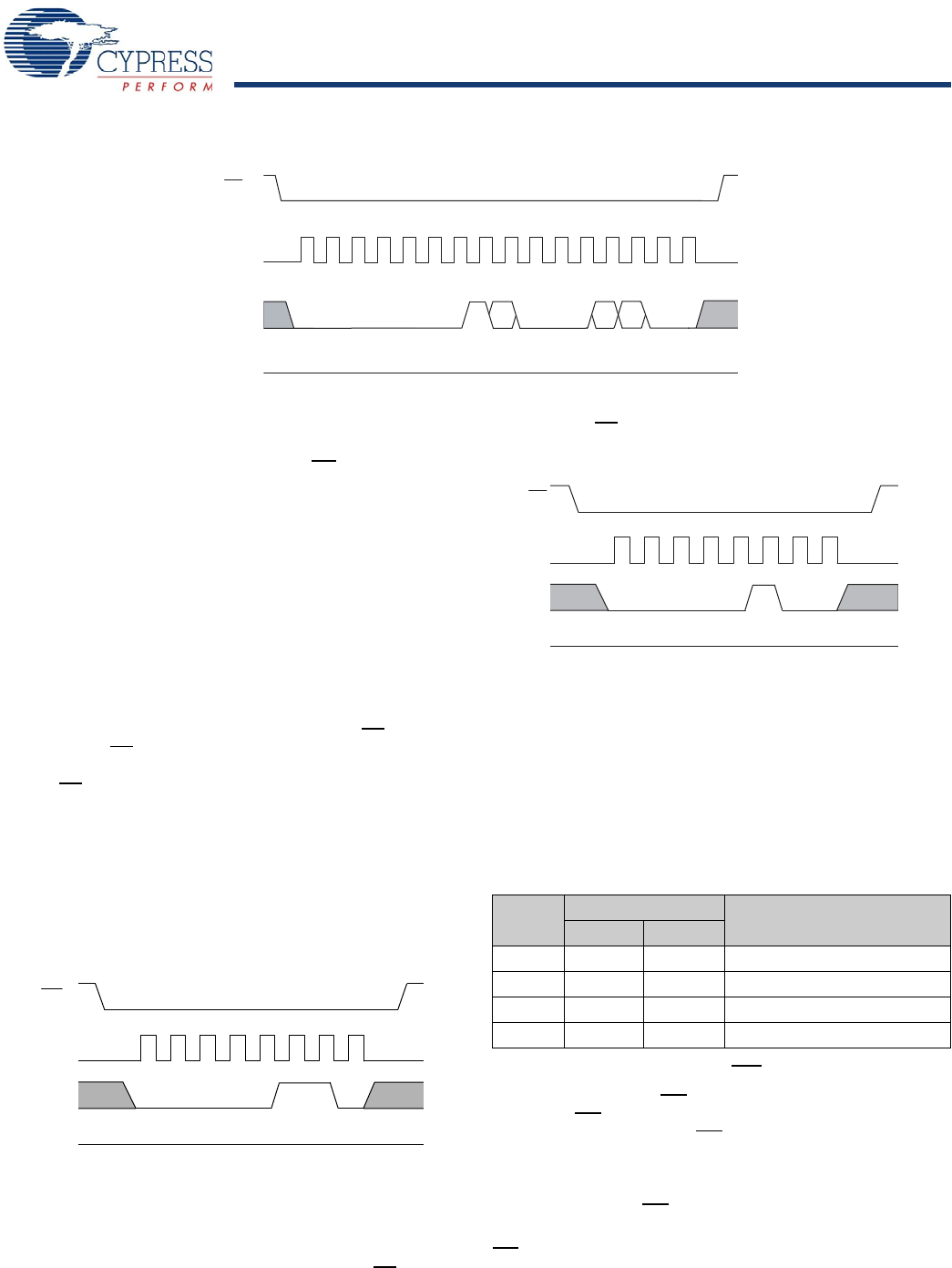
Figure 7. Write Status Register (WRSR) Instruction Timing
CS
SCK
SO
01234567
SI
0000000
1
MSB
LSB
0
0
D2
D3
0
00D7
HI-Z
012345 67
Opcode
Data in
Figure 8. WREN Instruction
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
CS
SCK
SI
SO
Hi-Z
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Figure 9. WRDI Instruction
Table 5. Block Write Protect Bits
Level
Status Register Bits
Array Addresses Protected
BP1 BP0
0 0 0 None
1 (1/4) 0 1 0x18000-0x1FFFF
2 (1/2) 1 0 0x10000-0x1FFFF
3 (All) 1 1 0x00000-0x1FFFF
0 00 00 1 00
CS
SCK
SI
SO
Hi-Z
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
[+] Feedback


















