CYV15G0404DXB
Independent Clock Quad HOTLink II™
Transceiver with Reclocker
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-02097 Rev. *B Revised December 14, 2007
Features
■ Quad channel transceiver for 195 to 1500 MBaud serial
signaling rate
❐ Aggregate throughput of up to 12 Gbits/second
■ Second-generation HOTLink
®
technology
■ Compliant to multiple standards
❐ SMPTE-292M, SMPTE-259M, DVB-ASI, Fibre Channel, ES-
CON, and Gigabit Ethernet (IEEE802.3z)
❐ 10 bit uncoded data or 8B/10B coded data
■ Truly independent channels
❐ Each channel is able to:
• Perform reclocker function
• Operate at a different signaling rate
• Transport a different data format
■ Internal phase-locked loops (PLLs) with no external PLL
components
■ Selectable differential PECL compatible serial inputs per
channel
❐ Internal DC restoration
■ Redundant differential PECL compatible serial outputs per
channel
❐ No external bias resistors required
❐ Signaling rate controlled edge rates
❐ Source matched for 50Ω transmission lines
■ MultiFrame™ Receive Framer provides alignment options
❐ Comma or full K28.5 detect
❐ Single or multibyte Framer for byte alignment
❐ Low latency option
■ Selectable input and output clocking options
■ Synchronous LVTTL parallel interface
■ JTAG boundary scan
■ Built In Self Test (BIST) for at-speed link testing
■ Link quality indicator by channel
❐ Analog signal detect
❐ Digital signal detect
■ Low power 3W at 3.3V typical
■ Single 3.3V supply
■ 256 ball thermally enhanced BGA
■ 0.25μ BiCMOS technology
■ JTAG device ID ‘0C811069’x
Functional Description
The CYV15G0404DXB Independent Clock Quad HOTLink II™
Transceiver is a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communica-
tions building block enabling the transfer of data over a variety of
high speed serial links including SMPTE 292, SMPTE 259, and
DVB-ASI video applications. The signaling rate can be anywhere
in the range of 195 to 1500 MBaud for each serial link. Each
channel operates independently with its own reference clock
allowing different rates. Each transmit channel accepts parallel
characters in an input register, encodes each character for
transport, and then converts it to serial data. Each receive
channel accepts serial data and converts it to parallel data,
decodes the data into characters, and presents these characters
to an output register. The received serial data can also be
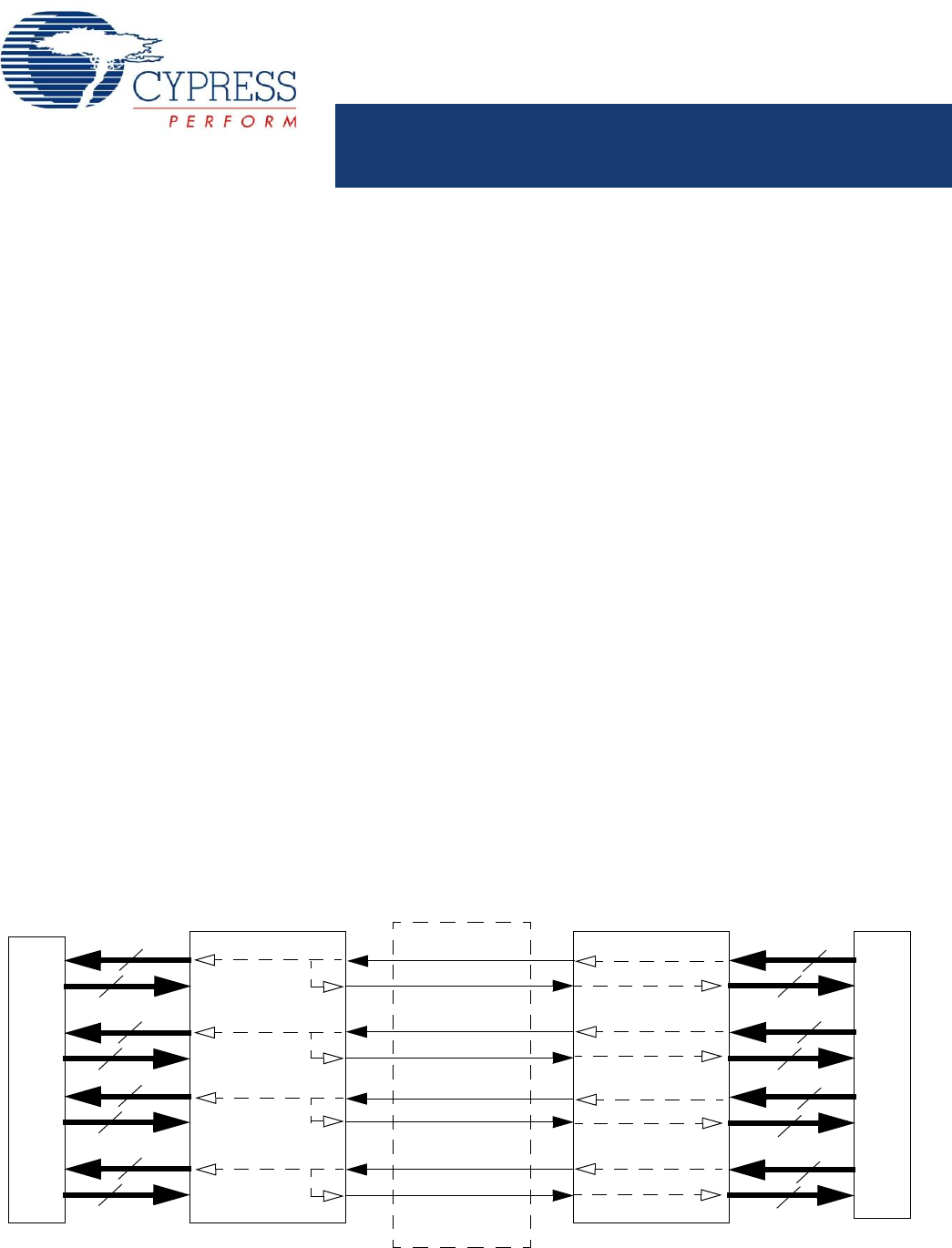
reclocked and retransmitted through the serial outputs. Figure 1
illustrates typical connections between independent video
coprocessors and corresponding CYV15G0404DXB chips.
Figure 1. HOTLink II™ System Connections
Video Coprocessor
Serial Links
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
Video Coprocessor
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
Serial Links
Serial Links
Serial Links
Cable
Connections
Independent
CYV15G0404DXB
Independent
Reclocker
Reclocker
Channel
CYV15G0404DXB
Channel
[+] Feedback [+] Feedback
