482 Configuring Routing
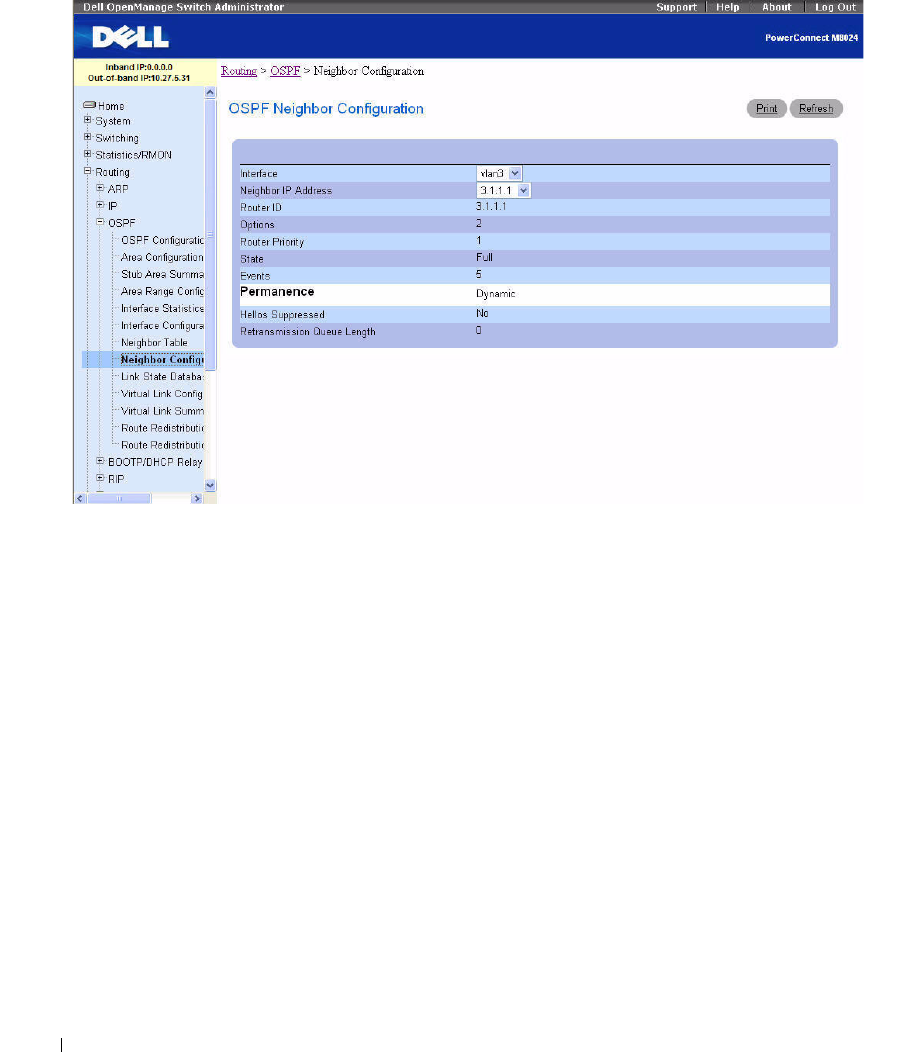
Figure 9-13. OSPF Neighbor Configuration
The OSPF Neighbor Configuration page contains the following fields:
•
Interface
— Select the VLAN interface on which routing is enabled from the drop-down menu.
•
Neighbor IP Address
— Select the IP Address of the neighbor for which data is to be displayed.
•
Router ID
— A 32-bit integer in dotted decimal format that identifies the neighbor router.
•
Options
— The optional OSPF capabilities supported by the neighbor. The OSPF Options field is
present in OSPF Hello packets, Database Description packets, and all link-state advertisements. The
Options field enables OSPF routers to support (or not support) optional capabilities, and to
communicate their capability level to other OSPF routers. Through this mechanism, routers of
differing capabilities can be mixed within an OSPF routing domain. The Options value is a bitmap,
and it signifies the capability of the neighbor.
•
Router Priority
— Displays the OSPF priority for the specified neighbor. The priority of a neighbor is a
priority integer from 0 to 255. A value of 0 indicates that the router is not eligible to become the
designated router on this network.
•
State
— The state of a neighbor can be the following:
–
Down
— This is the initial state of a neighbor conversation. It indicates that there has been no
recent information received from the neighbor. On NBMA networks, Hello packets may still be
sent to Down neighbors, although at a reduced frequency.


















