All about graphics
ELSA ERAZOR II and ELSA VICTORY Erazor LT
16
3D Interfaces
Software interfaces, including 3D interfaces, are known as APIs (Application Program
Interface). The question is what are these interfaces used for, and how do they work.
In simple terms: They make developers' work easier. The methods by which the various
interfaces function, are comparable: In the past it was necessary to address the various
hardware components directly in programming if you wanted to exploit their capabilities
to the full. The APIs are a kind of translator operating between the hardware and the
software.
The specification of standard definitions was the precondition for the proper function of
these translation routines. These definitions are implemented by the hardware manufac-
turers during development and optimized for the hardware concerned. Developers can
implement complex procedures relatively easily by using these definitions. They can use
a uniform command set when programming and do not need to know the characteristics
specific to the hardware.
What APIs Are Available?
There are a good dozen more or less commonly found 3D APIs. However, in recent years,
two formats have established themselves as the favorites: Direct 3D and OpenGL. ELSA
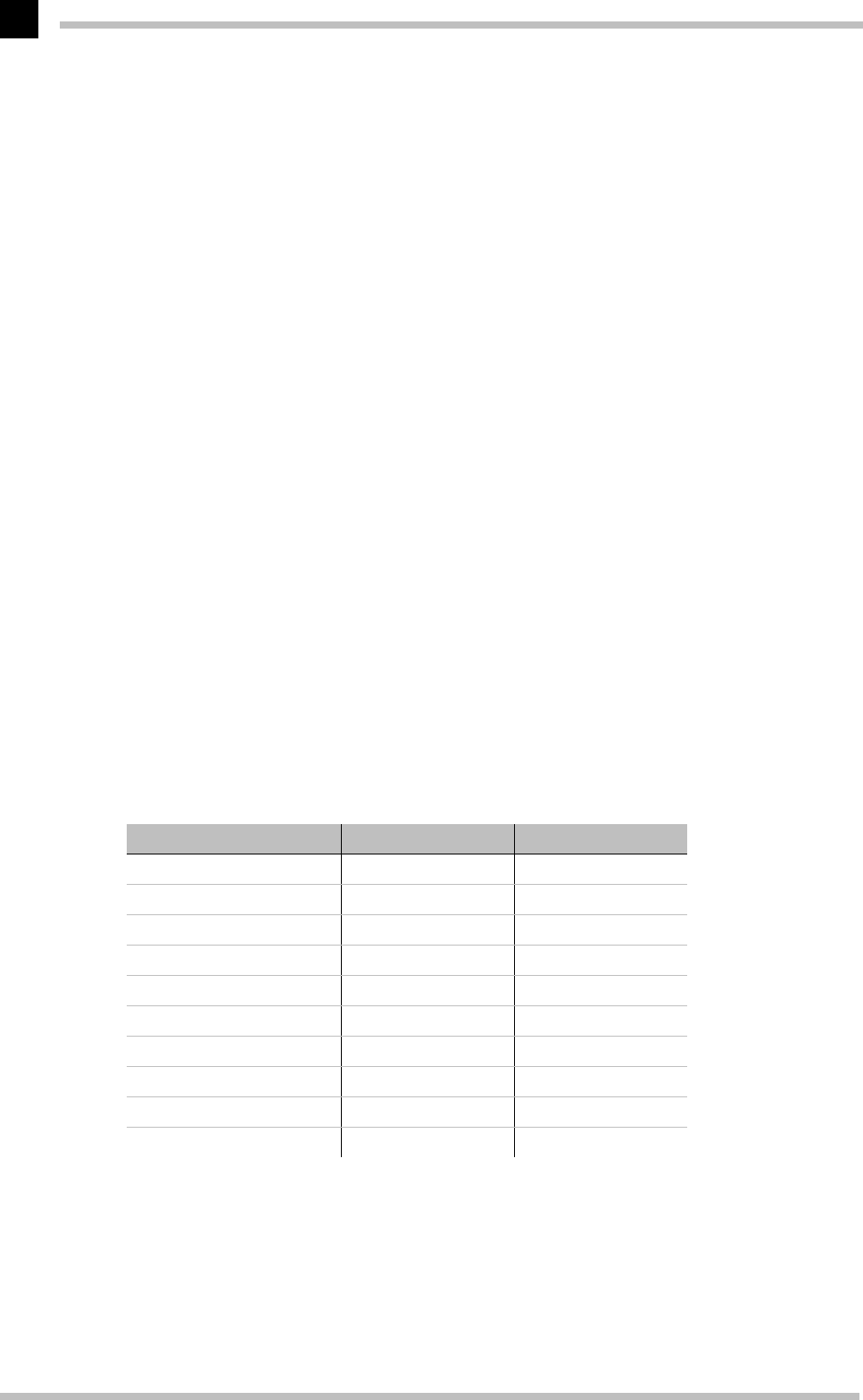
graphics boards support these commonly found 3D interfaces. The functional differences
between the interfaces are slight, as is shown by the table below. The decisive ques-
tions for the user concern extensibility, flexibility and possible portability to existing
applications.
Direct 3D
As a development of Mode X and DirectDraw under Windows 3.1x, Direct 3D is a branch
of the DirectX multimedia family which was developed directly for Windows 95 to accel-
Function Direct 3D OpenGL
Alpha blending
Texture mapping
MIP mapping
Video motion mapping
˿
Fogging
Anti-aliasing filter
Flat shading
Gouraud shading
Phong shading
˿˿
Stencil buffer
˿


















