Cable Tests
Introduction
4
4-7
The symptoms of a split pair range from non-existent to a
complete lack of communication. In some cases a split
pair cable may work just fine for 10BASE-T but not at all
for 100BASE-TX.
3
6
4
5
3
6
4
5
ace406f.eps
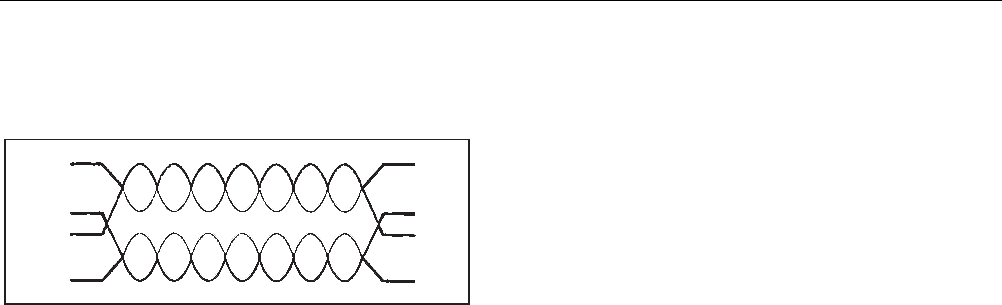
Figure 4-5. Split Pair
A split pair cannot be identified with a conventional
wiremap test because it is the wire pairing that is incorrect
rather than the physical connection. Another technique
must be used.
The most common method of identifying a split pair is by
measuring the Near End Crosstalk (NEXT). This is a very
reliable method but, unfortunately, it requires the use of a
remote unit at the far end. The Network Assistant uses
another equally reliable method that does not require a
remote unit at the far end (except in the case of short
cable lengths). The Network Assistant identifies split pairs
by measuring the characteristic impedance of each wire
pair. A split pair’s characteristic impedance is much
greater than the impedance of correctly paired wires.
Cable Length
The 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX cabling specifications
limit the maximum device-to-device cable length to 100
meters. There are many ways to measure a cable length;
the Network Assistant uses a very accurate method called
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR).
The TDR method works much like a radar system that
emits a pulse of electrical energy and then interprets the
reflected electrical energy. To measure the length of a
cable using the TDR method, a pulse of electrical energy
is sent down a wire pair, the reflected electrical energy is
interpreted to get the time delay between the transmitted
and reflected pulse, and the length of the cable is
computed using the cable’s Nominal Velocity of
Propagation (NVP).
The NVP is a value for how fast a pulse travels down a
given cable. Cable manufacturers specify how fast
electricity travels down a cable as a percentage of the
speed of light (186,000 miles/second or 300,000,000
meters/second). A cable with an NVP of 72, for example,
means that electricity travels at 72% of the speed of light
along the cable.