Configuring the FortiGate unit Preventing the public interface from responding to ping requests
FortiGate-50A/50B, FortiWiFi-50B and FortiGate-100 FortiOS 3.0 MR4 Install Guide
01-30004-0265-20070831 35
Transparent mode
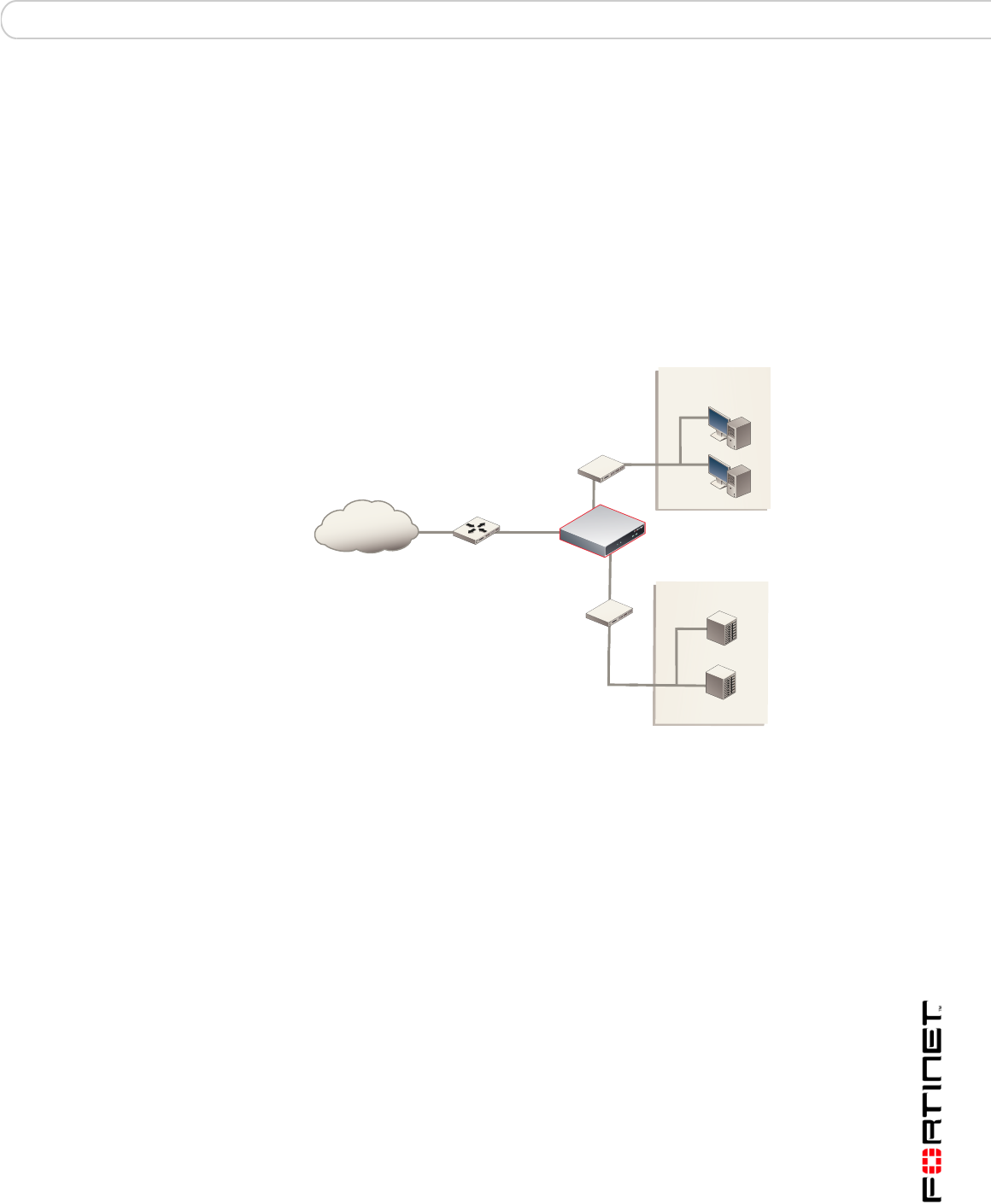
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit is invisible to the network. Similar to a
network bridge, all FortiGate interfaces must be on the same subnet. You only
have to configure a management IP address so that you can make configuration
changes. The management IP address is also used for antivirus and attack
definition updates.
You typically use the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode on a private network
behind an existing firewall or behind a router. The FortiGate unit performs firewall
functions, IPSec VPN, virus scanning, IPS web content filtering, and Spam
filtering.
Figure 10: Example Transparent mode network configuration for a FortiGate-100
Preventing the public interface from responding to ping
requests
The factory default configuration of your FortiGate unit allows the default public
interface to respond to ping requests. The default public interface is also called
the default external interface, and is the interface of the FortiGate unit that is
usually connected to the Internet.
For the most secure operation, you should change the configuration of the
external interface so that it does not respond to ping requests. Not responding to
ping requests makes it more difficult for a potential attacker to detect your
FortiGate unit from the Internet.
A FortiGate unit responds to ping requests if ping administrative access is
enabled for that interface. You can use the following procedures to disable ping
access for the external interface of a FortiGate unit. You can use the same
procedure for any FortiGate interface. You can also use the same procedure in
NAT/Route or Transparent mode.
Internal network
Internal
Internet
Router
FortiGate-100
External
DMZ
Internal
DMZ network
Web Server
Mail Server


















