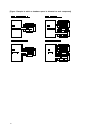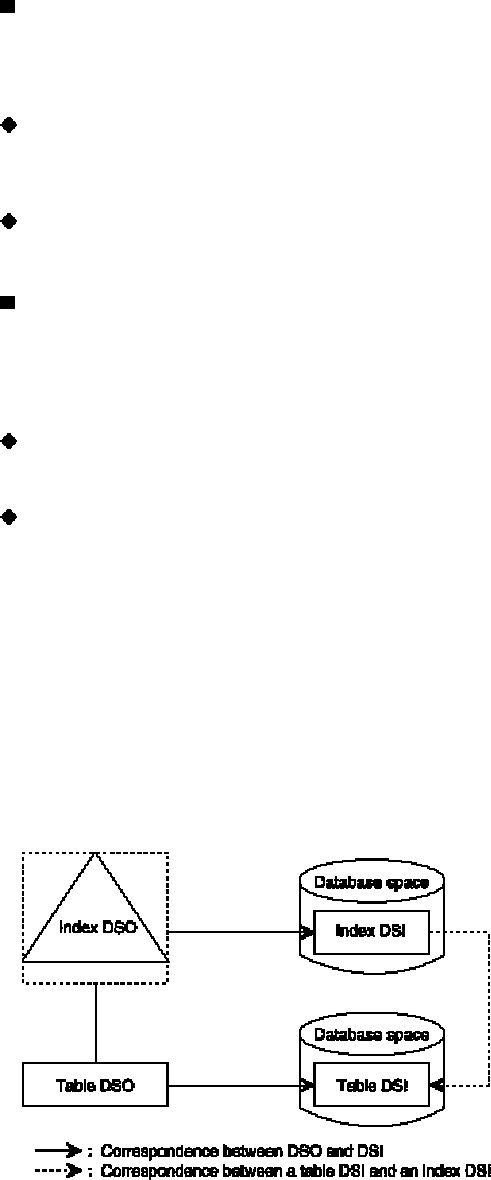
1.2.3 Storage structure
The storage structure consists of DSOs and DSIs.
DSO
A DSO defines the storage structure of the data for a base table. The two types of DSOs are as follows:
· Table
· Index
Table DSO
A table DSO defines the type of storage structure for storing data, and, if data is subdivided for storage, the
subdivision method.
Index DSO
An index DSO defines how the index is created for the table.
DSI
A DSI defines an area for storing base table data so that it can be allocated in a database space. The two types of
DSIs are as follows:
· Table
· Index
Table DSI
A table DSI defines an area for storing data so that it can be allocated in a database space.
Index DSI
An index DSI defines an area for storing index data added to a table so that it can be allocated in a database space.
A DSI associates a table or index with a database space.
DSOs and DSIs can be related in either a 1:1 or 1:n correspondence. If a 1:n correspondence exists, table data is
subdivided for storage, and rules for splitting the data are defined in the DSO. Figure: Example in which DSOs and
DSIs are associated in a 1:1 correspondence is an example in which table data is stored without being split. Figure:
Example in which DSOs and DSIs are associated in a 1:n correspondenceis an example in which table data is
subdivided for storage. An index DSI is defined for a table DSI. If table data is subdivided for storage, an index DSI
must be defined for each table DSI.
[Figure: Example in which DSOs and DSIs are associated in a 1:1 correspondence]
8