1.4 Link layer
C141-C013 47
1.4.2 Primitive sequences
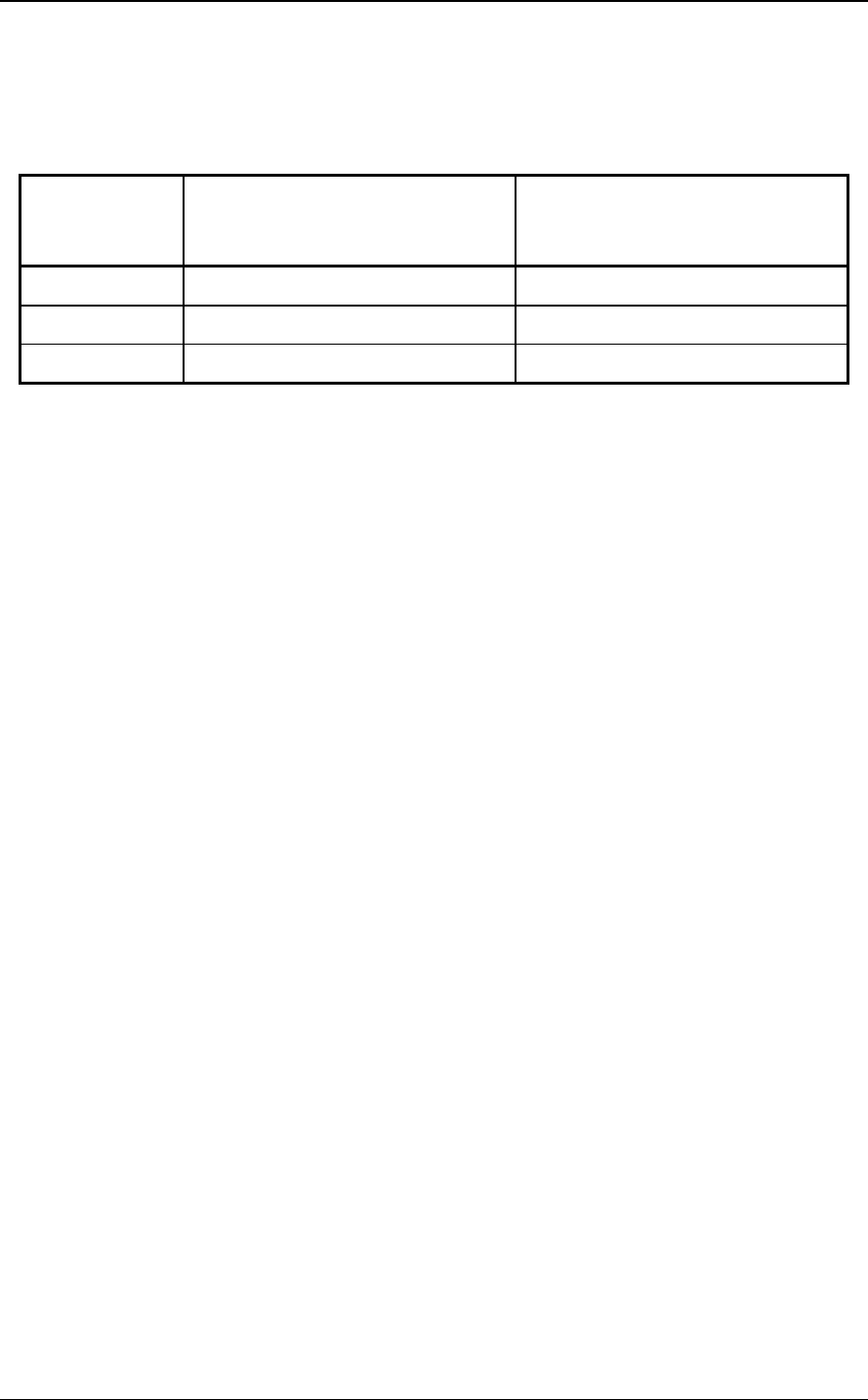
Table 1.12 summarizes the types of primitive sequences.
Table 1.12 Primitive sequences
Primitive
sequence type
Number of times the transmitter
transmits the primitive to transmit
the primitive sequence
Number of times the receiver
receives the primitive to detect the
primitive sequence
Single 1 1
Triple 3 3
Redundant 6 3
Any number of ALIGNs and NOTIFYs may be sent inside primitive sequences
without affecting the count or breaking the consecutiveness requirements. Rate
matching ALIGNs and NOTIFYs shall be sent inside primitive sequences inside
of connections if rate matching is enabled.
1.4.3 Primitives not specific to type of connections
1.4.3.1 AIP (Arbitration in progress)
AIP is sent by an expander device after a connection request to specify that the
connection request is being processed and specify the status of the connection
request.
A drive performs the following processing when an AIP primitive is received:
1) When the drive receives an AIP primitive after sending the OPEN frame, the
drive initializes the open timer held in the drive, and restarts it.
2) When the drive receives an AIP primitive before sending the OPEN frame,
the received AIP primitive is discarded.
3) In a case of OPEN cross (a case where both the drive and initiator send the
OPEN frame), when the drive receives an AIP primitive after sending the
OPEN frame and, then, receives the OPEN frame from the expander, the
drive does not perform the arbitration fairness procedure. Instead, the
attempt from the drive is treated as unsuccessful, and the drive sends the
OPEN_ACCEPT or an OPEN_REJECT primitive.
1.4.3.2 ALIGN
ALIGNs are used for:
a) OOB signals;
b) character and dword alignment during the speed negotiation sequence;
c) clock skew management after the phy reset sequence;
d) rate matching during connections; and


















