The advantage of tier 3 is that you should be able to provide a service to your
users quite rapidly. You must assess whether the loss of data will prevent your
company from continuing in business.
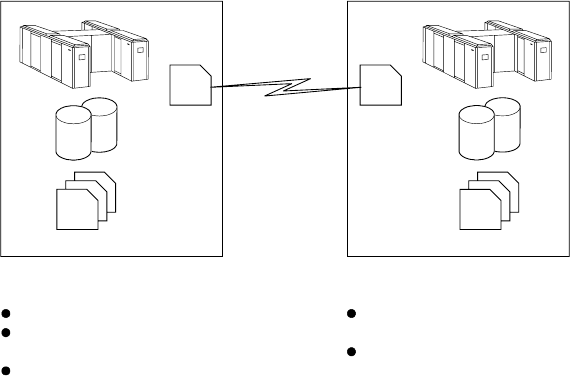
Figure 20 summarizes the tier 3 solution.
Tier 3 is similar to tier 2. The difference is that data is electronically transmitted to
the hot site. This eliminates physical transportation of data and the off-site storage
warehouse. The same process is used to backup the data, so the same primary site
availability issues exist in tier 3 as in tiers 1 and 2.
The benefits of tier 3 are:
v Faster recovery, as the data does not have to be retrieved from off-site and
down-loaded.
v No need to ship the backups manually to a warehouse and store them.
The drawbacks are the cost of reserving the DASD at the hot standby site, and that
you must have a link to the hot site, and the required software, to transfer the
data.
Procedures and documentation still have to be available at the hot site, but this can
be achieved electronically.
Tier 0–3 solutions
Tiers 0 to 3 cover the disaster recovery plans of many CICS users. With the
exception of tier 0, they employ the same basic design using a point-in-time copy
of the necessary data. That data is then moved off-site to be used when required
after a disaster.
Figure 21 on page 229 summarizes the solutions for tiers 0 through 3, and shows
the approximate time required for a recovery with each tier of solution.
Approach
Backups kept off-site
Procedures and inventory
off-site
Recovery - restore system
and data, reconnect to
network
Recovery
Standby site, plus bulk
data transfer costs
Recovery in hours
Standby Site
Figure 20. Disaster recovery tier 3: electronic vaulting
228 CICS TS for z/OS 4.1: Recovery and Restart Guide


















