Special RS/6000 SP Topics 193
impact of servicing a local I/O request through VSD relative to the normal
VMM/LVM pathway is very small. IBM supports any IP network for VSD, but
we recommend the switch for performance.
VSD provides distributed data access, but not a locking mechanism to
preserve data integrity. A separate product such as Oracle Parallel Server
must provide the global locking mechanism.
9.3.2 Recoverable Virtual Shared Disk
Recoverable Virtual Shared Disk (RVSD) adds availability to VSD. RVSD
allows you to twin-tail disks, that is, physically connect the same group of
disks to two or more nodes, and provide transparent failover of VSDs among
the nodes. RVSD is a separately-priced IBM LPP.
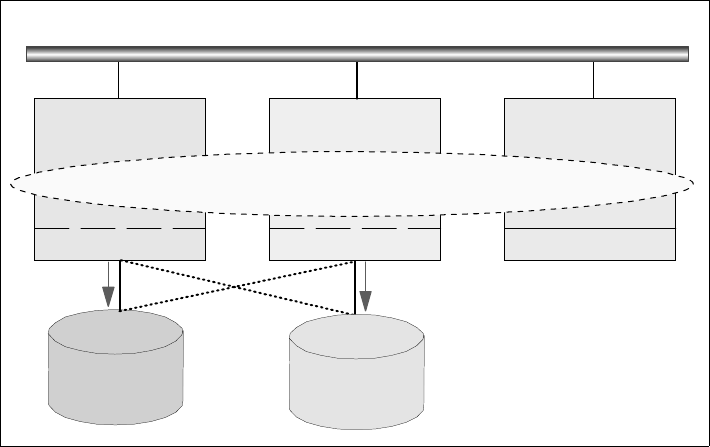
Figure 19. RVSD Function
With reference to Figure 19 above, Nodes X, Y, and Z form a group of nodes
using VSD. RVSD is installed on Nodes X and Y to protect VSDs rvsd_X and
rvsd_Y. Nodes X and Y physically connect to each other’s disk subsystems
where the VSDs reside. Node X is the primary server for rvsd_X and the
secondary server for rvsd_Y, and vice versa for Node Y. Should Node X fail,
RVSD will automatically fail over rvsd_X to Node Y. Node Y will take
ownership of the disks, varyon the volume group containing rvsd_X and make
the VSD available. Node Y then serves both rvsd_X and rvsd_Y. Any I/O
Node Y
Node X
Node Z
VSD
VSD VSD
VSD Server VSD Server VSD Client
rvsd_X
rvsd_Y
rvsd_X
(lv_X)
rvsd_Y
(lv_Y)
Fast IP Network


















