536EX Chipset Developer’s Manual 9
Intel Confidential
Introduction
When the controllerless chipsets are used with MS-DOS* applications, however, a UART
emulation is required. Intel provides an additional driver called Intelsdb.VxD, which includes a
UART emulation. Please refer to Section 9.1, “UART Emulation in the Controllerless Modem” on
page 92 for an explanation of the 536EX UART emulation. The Intelsdb.VxD driver interacts
directly with the VCOMM.VxD driver using the Win16 and Win32 Communication APIs.
1.2 V.90/V.92 and V.34 Data Modes
The 536EX chipset defaults to the V.90 or V.92 mode depending on the driver version. The V.90/
V.92 mode allows receive data rates of up to 56,000 kbps over the PSTN (public switched
telephone network) only in connections with equipment-compatible ISPs (Internet Service
Providers); however, FCC regulations limit receive speeds to 53,333 kbps due to excessive power
demands at higher speeds. In modem-to-modem connections, V.90/V.92 mode falls back to V.34
mode in both the transmit and receive directions. The chipsets implement all data rates and
modulation schemes for ITU-T (International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunications)
standards V.34, V.32 bis, V.32, V.22 bis, V.22, V.21, Bell 212A, and Bell 103.
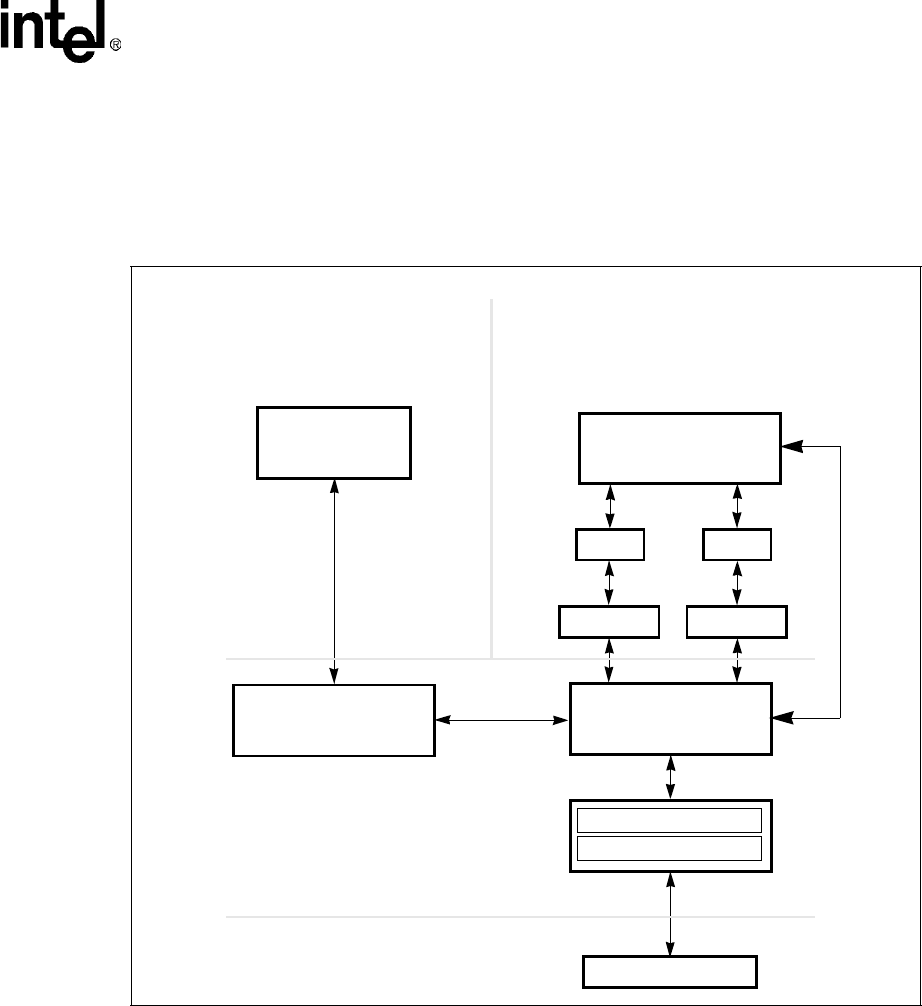
Figure 2. VxD Mini Port Driver Block Diagram
MS-DOS
APPLICATION
WINDOWS
APPLICATION
TAPI
Win 16
Unimodem COMM.DRV
VCOMM.VXD
HaM Port Driver
Interrupt Services
Chipset Hardware
Intelsdb.VXD
SYSTEM VIRTUAL MACHINE
NON-SYSTEM
VIRTUAL MACHINE
MS-DOS SHELL APPLICATION
OR DRIVER


















