21
Maintenance
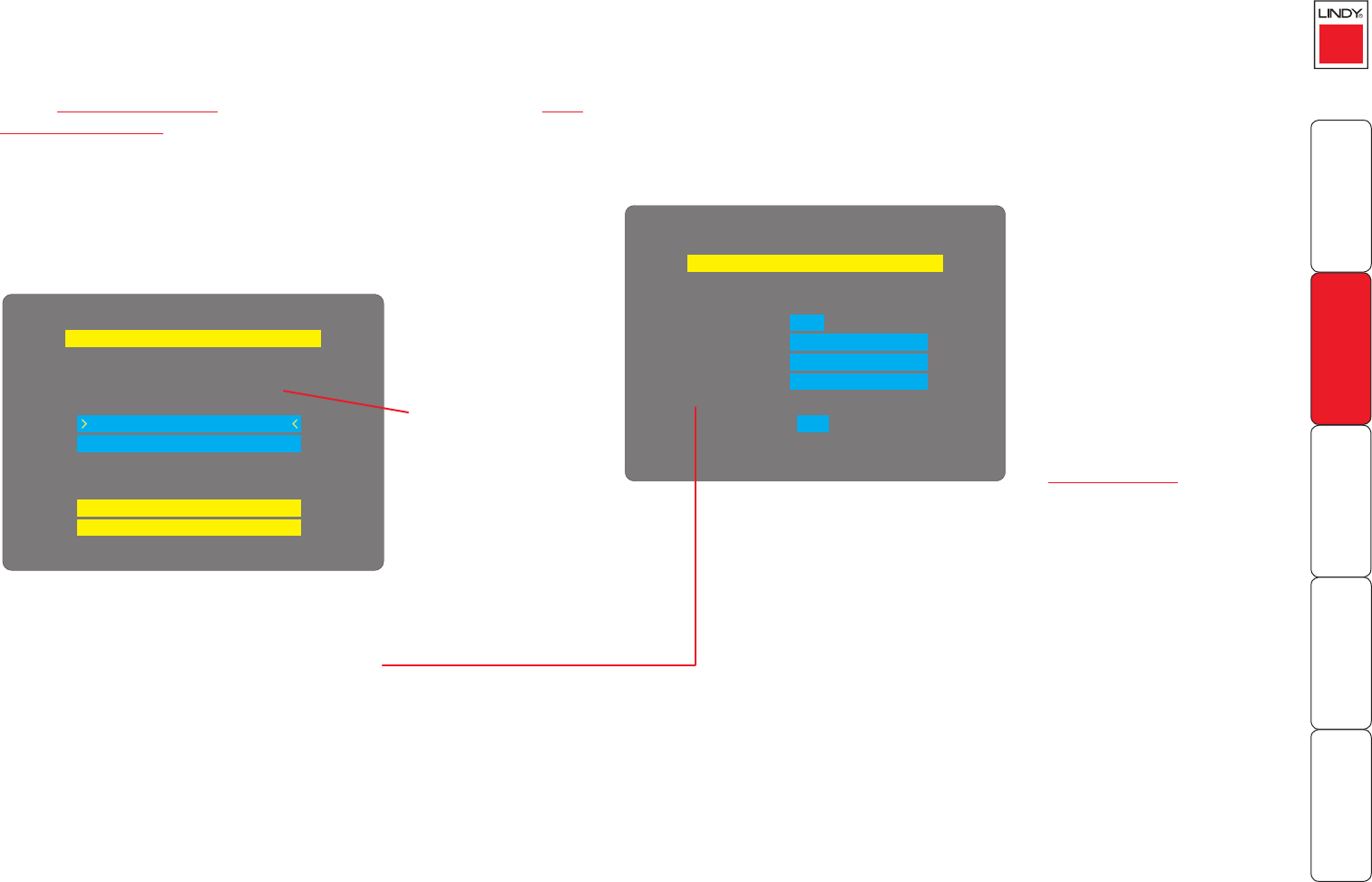
Reset Configuration
return to normal operation.
Configure Network
Put option switch 1 up t
o
To upgrade unit, visit:
http://192.168.42.154
Network Config
Net Mask 255.255.255.0
192.168.42.154
No
Gateway
OK
IP Address
00:0F:58:00:00:04
Use DHCP
MAC Address
Performing a ash upgrade
CPU IP is fully recongurable via ash upgrade.
To perform a ash upgrade
1 Using a remote connection, log on as the admin user and access the Unit
conguration page to determine the current rmware version of the CPU
IP unit.
2 Please contact LINDY Support to get the latest rmware revision.
3 Power down the CPU IP unit. At the rear of the unit, adjacent to the power
input socket, click mini switch 1 to its ON (down) position.
4 Re-apply power to the CPU IP. On the locally connected monitor you should
see a Maintenance menu:
The Maintenance menu should display the current network address
of the CPU IP.
• If the current network address is incorrect then select
the ‘Congure network’ option to change it:
5 Use the web browser (not the VNC viewer) on the previously used remote
system, connect to the network address shown in the local Maintenance
menu.
6 Follow the on screen instructions to upload the rmware le (previously
obtained from LINDY) to the CPU IP.
IMPORTANT: Wait until the upgrade is complete.
7 When the upload is complete and conrmed on screen, log off the remote
system and then power down the CPU IP.
8 At the rear of the unit, return the mini switch 1 to its OFF position and then
re-apply power.
MAC address
Media Access Control address – this
is the unique and unchangeable code
that was hard coded within your CPU IP
unit when it was built. It consists of six
2-digit hexadecimal (base 16) numbers
separated by colons. A section of the
MAC address identies the manufacturer,
while the remainder is effectively the
unique electronic serial number of your
particular unit.
Use DHCP
When this option is selected, your CPU IP
will attempt to locate a DHCP server on
the network. If such a server is located, it
will supply three things to the CPU IP:
an IP address, an IP network mask (also
known as a Subnet mask) and a Gateway
address.
IP address
This is the identity of the CPU IP within
a network. It can either be entered
manually or congured automatically
using the DHCP option. When the DHCP
option is enabled, this entry is greyed
out.
Net mask
Also often called the ‘subnet-mask’, this
value is used alongside the IP address
to help dene a smaller collection (or
subnet) of devices on a network. In
this way a distinction is made between
locally connected devices and ones that
are reachable elsewhere, such as on the
wider Internet.
Gateway
This is the address of the device that links
the local network (to which the CPU IP
is connected) to another network such
as the Internet. Usually this is a network
switch or router and it will be used
whenever a device to be contacted lies
outside the local network.
Congure network option
Current network
address of the
CPU IP


















