Wireless-G PCI Adapter
Instant Wireless
®
Series
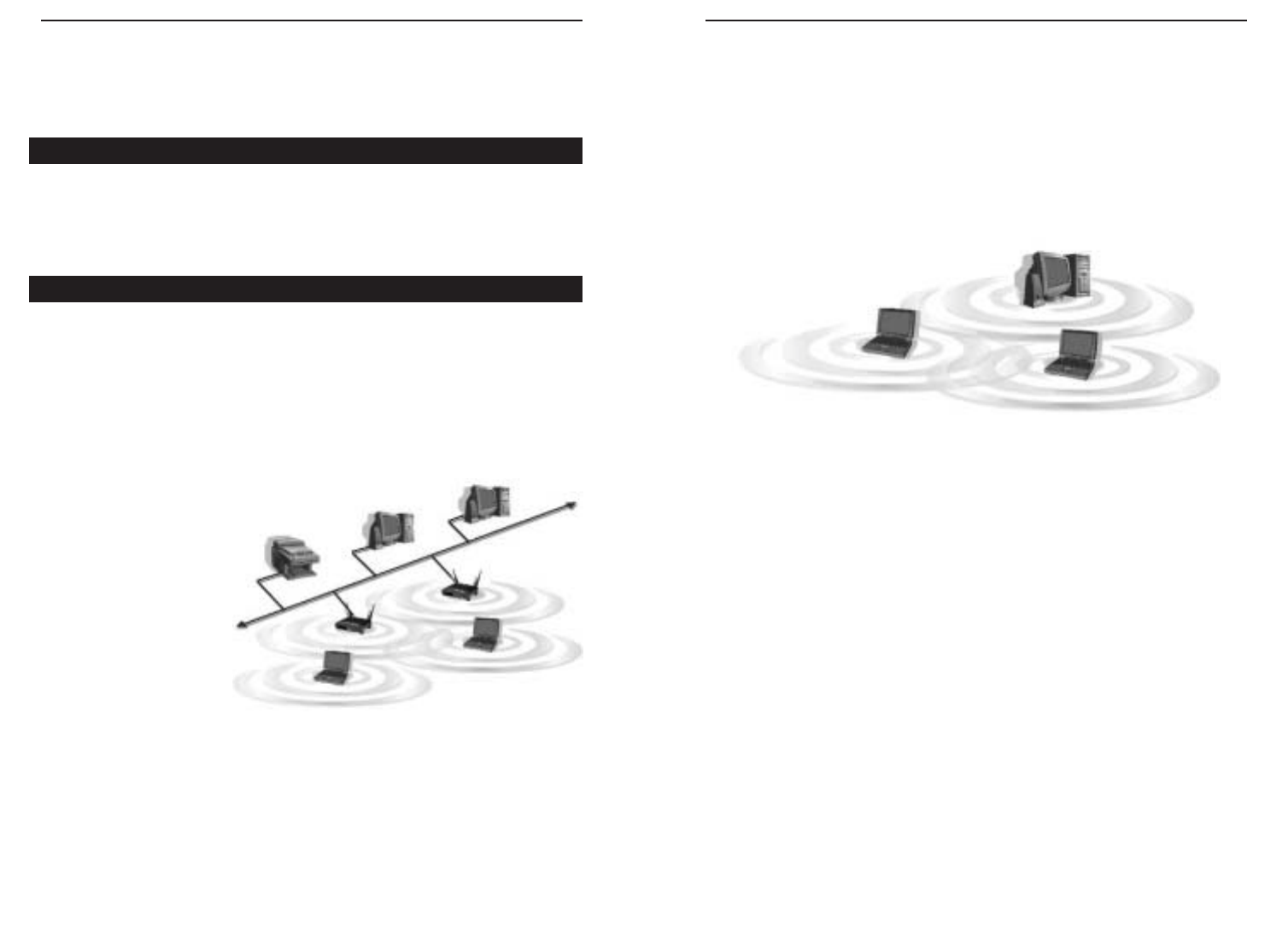
If the wireless network is relatively small and needs to share resources only
with the other computers on the wireless network, then the ad-hoc mode can
be used. (See Figure 2-2.) Ad-hoc mode allows computers equipped with wire-
less transmitters and receivers to communicate directly with each other, elimi-
nating the need for an access point. The drawback of this mode is that, in Ad-
Hoc mode, wireless-equipped computers are not able to communicate with
computers on a wired network. And, of course, communication between the
wireless-equipped computers is limited by the distance and interference direct-
ly between them.
32
Figure 2-2
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless
Network
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is exactly like a regular local area net-
work (LAN), except that each computer in the WLAN uses a wireless device to
connect to the network. Computers in a WLAN share the same frequency
channel and SSID, which is an identification name for wireless devices.
Unlike wired networks, wireless networks have two different modes in which
they may be set up: infrastructure and ad-hoc. In an infrastructure configu-
ration a WLAN and wired LAN communicate to each other through an access
point. In ad-hoc configuration, wireless-equipped computers communicate
directly with each other. Choosing between these two modes depends on
whether or not the wireless network needs to share data or peripherals with a
wired network or not.
If the computers on the
wireless network need to
be accessed by a wired
network or need to share a
peripheral, such as a print-
er, with the wired network
computers, the wireless
network should be set up
in infrastructure mode.
(See Figure 2-1.) The
basis of infrastructure
mode centers around an
access point, which serves
as the main point of communications between a wired and wireless network.
Access points transmit data to PCs equipped with wireless network adapters,
which can roam within a certain radial range of the access point. Multiple
access points can be arranged to work in succession to extend the roaming
range, and can be set up to communicate with your Ethernet (wired) hardware
as well.
Network Topology
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode
Figure 2-1


















