Chapter 3 – Using the Web Management Software
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MultiModem Wireless Modem with Ethernet Interface (S000375F) 38
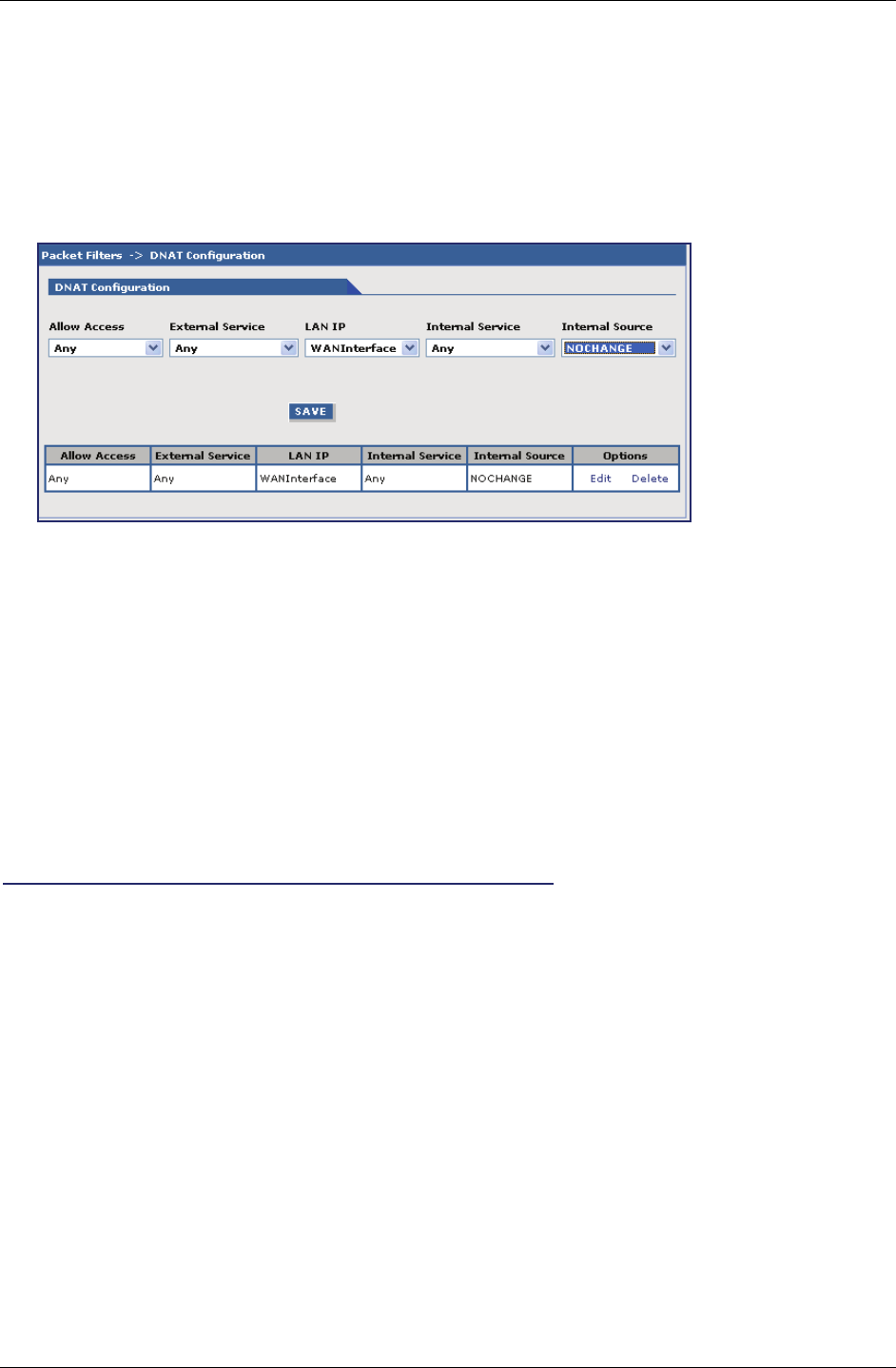
Packet Filters > DNAT Configuration
Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) is a process that allows the placing of servers within the protected
network and making them available for a certain service to the outside world. The DNAT process running of the
wireless modem/router translates the destination address of incoming packets to the address of the real network
server on the LAN. The packets are then forwarded.
You can Delete or Edit a DNAT rule after it has been defined and added by using the table at the bottom of the
screen.
Important Note: When adding rules, at least one host must be defined in the Network Configuration section.
DNAT Configuration
Allow Access: Select a network or host to which IP packets will be allowed and re-routed. The
network/host must be pre-defined in the Network Configuration section.
External Service: Select the External Service that you want allowed. The service must be defined in the
Service Configuration section.
LAN IP: Select the LAN IP to which the packets are to be diverted. Only one host can be
defined as the destination.
Internal Service: Select the Internal Service to be the destination.
Internal Source: Select the source address for packets that going to be sent. If you do not want to
change the address, select NOCHANGE.
Save Button: Click the Save button. The defined DNAT configuration is added and will display at
the bottom of the screen. Entries can be deleted or edited by clicking the Edit or the
Delete buttons.
Packet Filters > DNAT Example
Set Up DNAT and Port Forwarding to an Internal Device
Note: The internal device can be camera, meter, security device, etc.
Situation: Assume the device is on a LAN with an IP address of 192.168.2.100 and the port to access the
device is port 7700.
1. On the Network & Services > Network Configuration screen, set up the following parameters:
Name – Enter a name for the LAN device.
IP Address and Subnet Address – Enter the IP address and subnet address of the device.
Example: Name = MeterIP
IP Address = 192.168.2.100
Subnet Address = 255.255.255.255
Add – Click the Add button to save this configuration.
2. On the Network & Services > Service Configuration screen, define a service name. For this example,
the service will be a meter.
Name – Enter a name for the service (use a name that will identify the service for you).
Example: MeterPort
Protocol – Select a protocol.
Example: tcp/udp
S-Port / Client – Enter the source port for this service.
Example: 1:65535
D-Port / Server – Enter the destination port for this service.
Example: 7700
Add – Click the Add button to save this configuration.


















