Appendix B Serial Port Information
© National Instruments Corporation B-5 Serial Hardware and Software for Windows
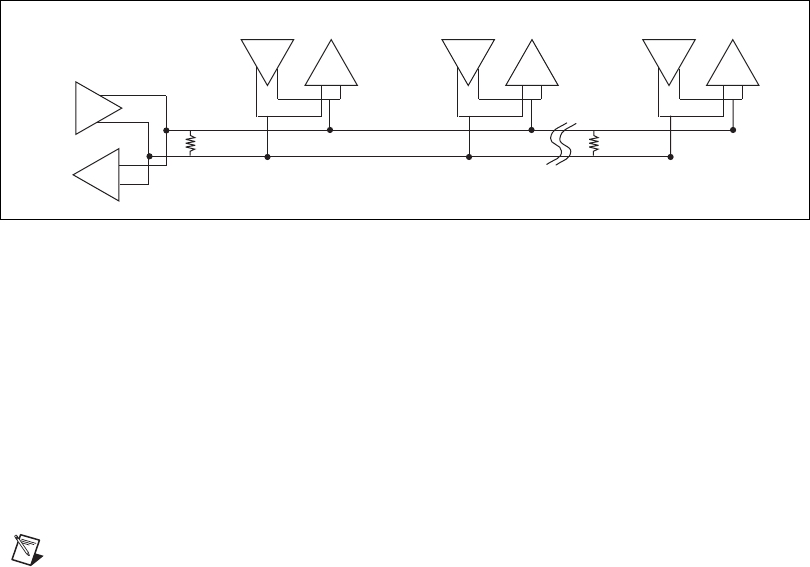
Termination
Because each differential pair of wires is a transmission line, you must
properly terminate the line to prevent reflections. A common method of
terminating a two-wire multidrop RS-485 network is to install terminating
resistors at each end of the multidrop network. If you daisy-chained
multiple instruments together, you need a terminating resistor at only the
first and last instruments. The terminating resistor should match the
characteristic impedance of the transmission line (typically 100 to 120 Ω).
You can order an optional DB-9 RS-485 termination connector that
contains embedded terminating resistors for easy termination from
National Instruments. For ordering information, contact National
Instruments.
Figure B-3 shows a multidrop network using terminating resistors.
Figure B-3. Multidrop Network Using Terminating Resistors
Bias Resistors
A transmission line enters an indeterminate state if no nodes are
transmitting on it. This indeterminate state can cause the receivers to
receive invalid data bits from noise picked up on the cable. To prevent a line
from receiving these data bits, force the transmission line into a known
state. To do so, install two 620 Ω bias resistors at one node on the
transmission line; doing so creates a voltage divider that forces the voltage
between the differential pair to be greater than 200 mV, the threshold
voltage for the receiver. You should install these resistors on only one node.
Note
Bias resistors are not available on the eight-port PCI-485 or eight-port PXI-8421.
MASTER
Slave 1
100 Ω
Slave 2 Slave n
100 Ω
Tx
Tx
Rx
Tx
Rx
Tx
Rx
Rx