Reference Manual for the 54 Mbps Wireless Router with Phone Adapter WGR826V
D-4 Wireless Networking Basics
202-10051-01, March 2005
2.
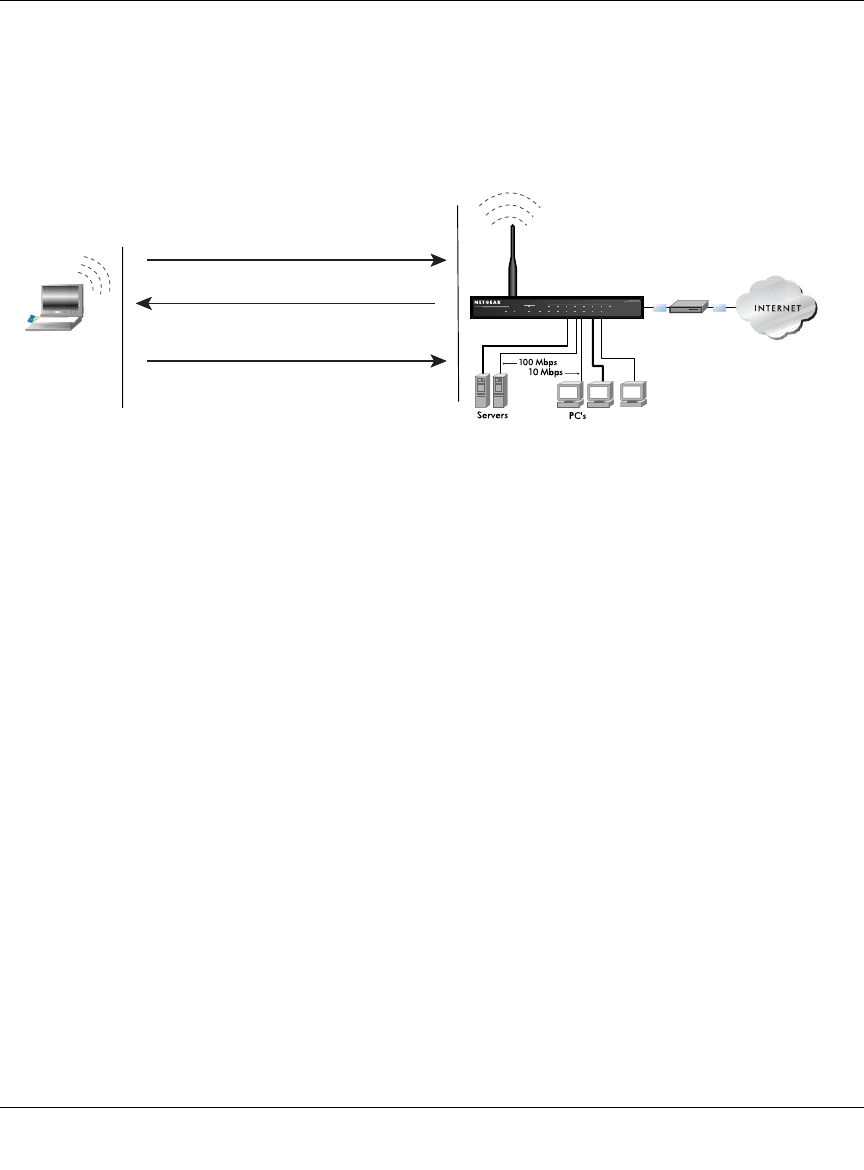
The access point authenticates the station.
3. The station associates with the access point and joins the network.
This process is illustrated below.
Figure D-1: Open system authentication
Shared Key Authentication
The following steps occur when two devices use Shared Key Authentication:
1. The station sends an authentication request to the access point.
2. The access point sends challenge text to the station.
3. The station uses its configured 64-bit or 128-bit default key to encrypt the challenge text, and
sends the encrypted text to the access point.
4. The access point decrypts the encrypted text using its configured WEP Key that corresponds
to the station’s default key. The access point compares the decrypted text with the original
challenge text. If the decrypted text matches the original challenge text, then the access point
and the station share the same WEP Key and the access point authenticates the station.
5. The station connects to the network.
If the decrypted text does not match the original challenge text (the access point and station do not
share the same WEP Key), then the access point will refuse to authenticate the station and the
station will be unable to communicate with either the 802.11 network or Ethernet network.
INTERNET LOCAL
ACT
12345678
LNK
LNK/ACT
100
Cable/DSL
ProSafeWirelessVPNSecurityFirewall
MODEL
FVM318
PWR TEST
WLAN
Enable
Access Point
1) Authentication request sent to AP
2) AP authenticates
3) Client connects to network
802.11b Authentication
Open System Steps
Cableor
DLSmodem
Client
attempting
to connect


















