Radius operation
21
The traditional Radius system is meant to
operate within a secure network, such as
intranet, because it does not require much skill
to capture radius packets and use faked packets
to provide false authentication information.
That’s why the WEP keys received from Radius
server are encrypted.
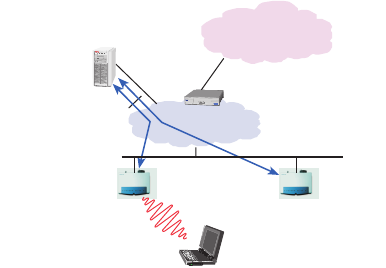
Radius security scheme has three to four
components. The network architecture of the
system can be seen in the figure below. The
first component is the client trying to perform
the authentication. Traditionally, this is a
laptop trying to set up a connection to
corporate modem pool via a dial-in connection
from the PSTN. On the WLAN scenario the
client is a laptop, or a wired PC using an
adapter, trying to set up a WLAN connection to
an Access Point.
The second component is the modem-pool
server that tries to find out if the user is valid
or not. The modem pool server tries to
authenticate the user against the central user
database by using the Radius protocol so
modem pool server is a Radius client described
Internet
Firewall
Intranet
Key server
(WEP keys,
certificates, etc.)
Secured
connection
Access Point Access Point


















