Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
6-7
8000-A2-GB26-10
January 1999
Network Problems
To provide a practical aid in the isolation and resolution of Layer 2 network
difficulties, the guidelines in this section provide information on troubleshooting a
generic network containing the devices found in most networks.
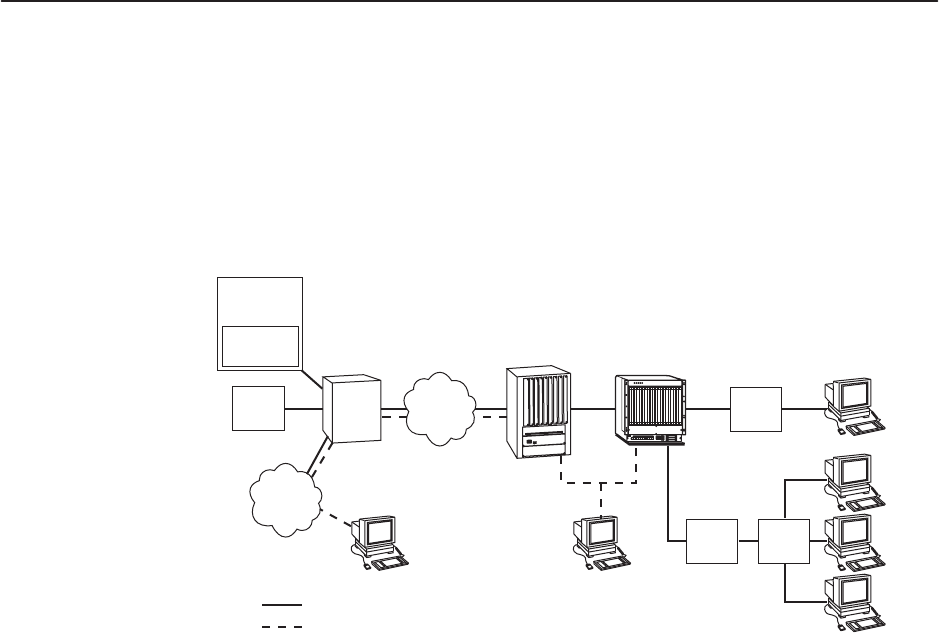
The illustration below shows the generic network addressed by this chapter.
99-16153a-01
O
I
Next Hop
Router
(NHR)
DSLAM Clients
NMS
WAN
HubSN
SN
ISP
IPC
WAN
Service Domain
Management Domain
ISP = Internet Service Provider
IPC = Interworking Packet Concentrator
NMS = Network Management System
SN = Service Node
NMS
ISP
Gateway
Router
These procedures assume that Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is used on
the link between the IPC and the next hop router (NHR).
High-Level Troubleshooting
The following high-level procedures help you isolate problems to a particular
segment of the network.
H For static clients, make sure the client can Ping its own IP address. This
confirms the IP address was successfully accepted by the client computer.
H Make sure the client’s default gateway is the same as the IP address for the
Bridge Virtual Interface (BVI) on the appropriate ISP router.
H An Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table may have invalid entries if a
recent configuration change took place anywhere on the network and not
enough time has passed for the entry to expire. Check the ARP tables on the
client, DSLAM, and router.
H Make sure a default route is configured on the MCC card (screen A-E-A).


















