\TANO
Transfer Network Analog Output Status
Type:
Network; Transfer
Product Rev
Syntax:
<!>n\mTANO<.i>
Units:
n = network server #
m = module #
i = analog output # on module “m” (for bit-select operation)
(The response represents volts DC.)
Range:
n = 1-6
m = 0-7
i = 1-2
Default:
n/a
Response:
1\1TANO:
1\1TANO.2:
*2.42,3.32
*3.32
See Also:
\ANO, [ \ANO ], NTIO, \TIO
6K 5.3
The
\TANO
command returns the voltage commanded at one of the network analog outputs (the voltage is commanded with
the
\ANO
command). The network server number and module number must precede the
\TANO
command (e.g.,
2\3ANO
reports the voltage commanded on all analog outputs on module 3 of network server 2).
If the status of a specific analog output is required, use the bit select operator (
.
). For example,
1\3TANO.2
reports the
voltage of analog output 2 on module 3 of network server 1.
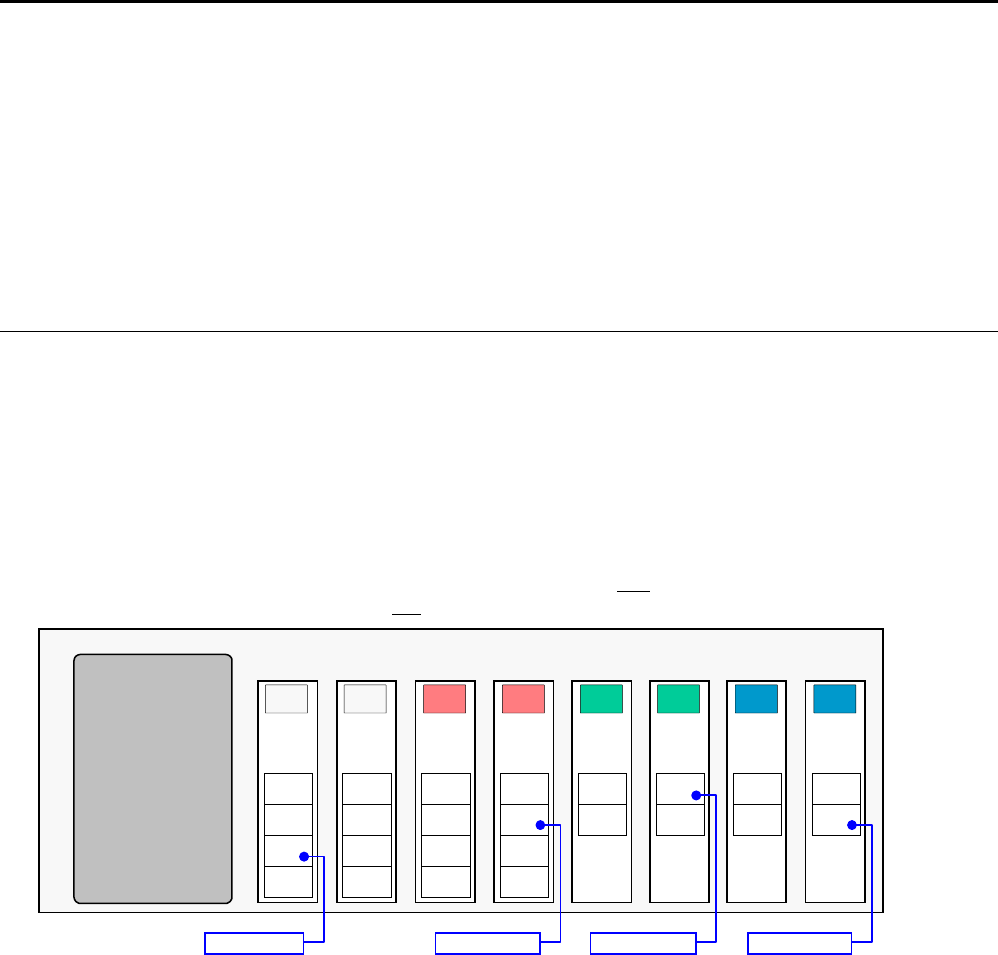
The controller addresses the OPTO22 I/O locations as follows:
Each I/O bit is addressed by its location on a specific module. (NOTE: I/O points are not addressed by an absolute
32-bit location on the OPTO22.) Digital input and output modules have four
I/O points, or channels, and are numbered
1-4. Analog input and output modules have two
I/O points, or channels, and are numbered 1-2.
Digital
Input
Module
Input
1
0
Input
2
Input
3
Input
4
Digital
Input
Module
Input
1
1
Input
2
Input
3
Input
4
Digital
Output
Module
Output
1
2
Output
2
Output
3
Output
4
Digital
Output
Module
Output
1
3
Output
2
Output
3
Output
4
Analog
Output
Module
Output
1
4
Output
2
Analog
Output
Module
Output
1
5
Output
2
Analog
Input
Module
Input
1
6
Input
2
Analog
Input
Module
Input
1
7
Input
2
EXAMPLE: OPTO22 is Network Server #2
2\0TIN.3 2\3TOUT.2 2\5TANO.1 2\7TANI.2
page 41


















