38
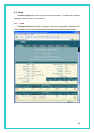
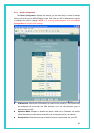
z VPI and VCI: Determine the unique data path your modem uses to communicate with
your ISP.
z Bridge: Enables or disables bridging between the device and your ISP.
z IGMP: Can be used to enable the WAN interface to pass Internet Group Management
Protocol messages it receives to the LAN PCs. You must enable the LAN or USB
interfaces for IGMP.
z IP Address and Subnet Mask: If your ISP has provided a public IP address to your LAN,
enter the address and the associated subnet mask in the boxes provided. (Note: In
bridge configurations, the public IP address may be entered on your PC rather than on
the ADSL/Ethernet router; check with your ISP.).
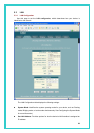
z Use DHCP: When enabled, your ISP will use DHCP to assign an IP address to the WAN
interface. When disabled, the ISP will either use another protocol, or you must manually
assign an IP address to it. See the appropriate WAN interface help topic for PPP or EoA
interfaces.
z Default Route: When enabled, specifies that the WAN interface specified above will be
used as the default route for your LAN. Whenever one of your LAN computers attempts
to access the Internet, the data will be sent via through this interface.
z Gateway IP Address: Specifies the IP address that identifies the ISP server through
which your Internet connection will be routed.
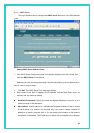
z PPP Username and Password: The username and password you use to log in to your
ISP. (Note: this is not the same as the user name and password you used to log in to
Configuration Manager.)
z Use DNS: Specifies whether the DNS server addresses that your LAN will use should be
supplied dynamically via the PPP connection each time you connect to the ISP.
If you click Disable, you must configure DNS addresses manually on each PC or in the
fields below.
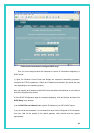
z Primary/Secondary DNS: Specifies the Primary and Secondary DNS server addresses
provided by your ISP.