Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Literature
Number Description
Application Notes
SCAA059
AC-Coupling Between Differential L
VPECL, L
VDS, HSTL, and CML
SCAA062
DC-Coupling Between Differential LVPECL, LVDS, HSTL, and CML
Part Number Description Price
*
Evaluation Modules (EVMs)
SN65LVDS31-32EVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS32 49.00
SN65LVDS31-32BEVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS32B 49.00
SN65LVDS31-33EVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS33 49.00
SN65LVDS386EVM SN65LVDS386 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65L
VDS387EVM
SN65L
VDS387 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65LVDS100EVM SN65LVDS100 Evaluation Module 99.00
SN65LVDS20EVM SN65LVDS20 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65CML20EVM
SN65CML20 Evaluation Module
49.00
SN65L
VCP22-23EVM
SN65L
VCP22 Evaluation Module
25.00
SN65LVDS122EVM SN65LVDS122 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65LVDS250EVM SN65LVDS250 Evaluation Module 49.00
Note: IBIS models are available at interface.ti.com
*
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars.
Literature
Number
Description
Application Notes
SLLA014A Low-Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) Design Notes (Rev. A)
SLLA030C Reducing Electromagnetic Interference with LVDS (Rev. C)
SLLA031A Using an LVDS Receiver with TIA/EIA-422 Data (Rev. A)
SLLA034A
Slew Rate Control of L
VDS Circuits (Rev
. A)
SLLA038B
Interface Circuits for TIA/EIA-644 (LVDS) (Rev. B)
SLLA053B Performance of LVDS with Different Cables (Rev. B)
SLLA054A
L
VDS Multidrop Connections (Rev
. A)
SLLA065
A Comparison of LinBiCMOS and CMOS Process T
echnologies in L
VDS ICs
SLLA082B Active Fail-Safe in TI's LVDS Receivers (Rev. B)
SLLA100 Increase Current Drive Using LVDS
SLLA101 Interfacing Different Logic with LVDS Receivers
SLLA103 LVPECL and LVDS Power Comparison
SLLA104 Suggestions for L
VDS Connections
SLLA105 DSP to DSP Link Using LVDS
SLLA107 Live Insertion with Differential Interface Products
SLLA147 Suitable LVDS Architectures
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
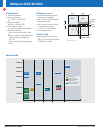
LVDS Family of Products
LVDS2
L
VDS9637
LVDS34
Singles
Transmitters Receivers Transceivers Repeaters/
Translators
Crosspoint
Switches
Up to 400 Mbps
Up to 630 Mbps
≥ 1 Gbps
Clock Distribution Devices
(See pg. 42 for table)
LVDS388A
LVDS386
C
DCLVD110
L
VDS108
LVDS104
L
VDS105
L
VDS117
LVDS116
L
VDS9638
LVDS179
LVDS180
L
VDS049
LVDS050
LVDS051
LVDS1050
CML100
LVDS100
LVDS101
LVDS16 LVP16
LVDS17 LVP17
LVDS18 LVP18
LVDS19 LVP19
LVDS20 LVP20
L
VDS22
LVCP22
LVCP23
LVDS122
L
VDS250
Duals
Quads
8 Channels
16 Channels
10 Channels
LVDS109
LVDS1
L
VDS389
LVDS387
LVDS047
LVDS31
LVDS3487
L
VDS391
LVDS048A/348
LVDS32/33
LVDS3486
L
VDS390
Design Considerations
S
ignaling Rate
—
TI offers repeaters/transla-
tors and crosspoint switches with signaling
r
ates up to 4.0 Gbps.
Jitter — Reducing jitter, the deviation of a
signal timing event from its ideal position,
has become a priority for ensuring reliability
in high-speed data buses.
Skew — Excessive skew, the time delta
between the actual and expected arrival
time of a clock signal, can limit the maximum
bandwidth performance and lead to data
s
ampling errors. Low skew specifications
make high-speed interconnect devices
e
xcellent for signal buffering.
Power Consumption — Low-voltage
differential signaling (LVDS) offers a low-power
alternative to ECL and PECL devices. Current-
mode drivers in LVDS produce a constant
current, which allows power consumption to
be relatively independent of frequency. The
constant current driver delivers about 3.5 mA
to a 100-W load.
Technical Information
• LVDS is based on the TIA/EIA-644A
standard conceived to provide a general-
purpose electrical-layer specification for
drivers and receivers connected in a
point-to-point or multidrop interface.
4
LVDS, xECL, CML
➔