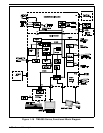
1.8.3 I/O Subsystem
The I/O ASIC on the Main Board and an SMC 37C665 GT Combo I/O
Controller Chip control all "AT"-type I/O peripherals. Two cascaded DMA
controllers and two cascaded interrupt processors on the I/O ASIC support
transfers between memory and the 8-bit and 16-bit peripherals (via the
Combo Controller). The supported I/O interfaces include:
• Internal Hard Disk Drive Interface - Provides control information and
data exchange (via an integrated drive electronics (IDE)-type interface)
between the computer and the system disk drive.
• Internal Floppy Diskette Drive Interface - Provides control and data
exchange between the computer and the 3.5 inch floppy diskette drive.
• Internal Pointing Device Interface- internal controller that interfaces the
built-in pointing device with the system processor.
• External Parallel Bi-Directional/ECP/EPP Compatible Interface -
Provides control information and data exchange between the computer
and external parallel peripheral devices via an external DB-25 Port (this
port is configured from the Setup program). The parallel port is
compatible with the port used in the PC-AT but also features the PS/2
like extended mode for bi-directional EPP/ECP operations.
• External Serial Port Interface- includes a 16550-compatible UART that
drives an external RS-232 port (configured from the Setup Program).
• External PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Port- six-pin Mini-DIN connector on the
rear of the Notebook which can attach to either an external PS/2
keyboard (or 101 keyboard with adapter), external PS/2 type mouse, or
external numeric keypad (only one of the three device types may
connect to the 6-pin connector).
1.8.4 AT Peripherals Subsystem
The interface between the system processor and the Floppy and Serial and
Parallel ports is provided by the FDC37C665GT combination controller.
1.8.5 Video Subsystem
The video subsystem, implemented on the Main Board and on the LCD
Display Unit, displays text, graphics and drives an external VGA port.
The video subsystem includes 2 MB RAM memory, 32-bit DRAM bus, and
separate display and memory clocks. An additional frame buffer/accelerator
DRAM increases the available memory bandwidth for CPU accesses. The
video section also uses additional levels of write FIFOs, a read cache, page
mode DRAM and full 32-bit bus access to produce a high performance video
system.
The CL-GD7542 video controller chip used in the TM5000 Notebooks also
supports multi-media capabilities using the MotionVideo
tm
Architecture
(MVATM). This feature permits integrating video clips or live video. In
1-32 General Description