UPS 225 - 275 kVA
User’s and Installation Guide
1027212
Revision B
41
4.2 Modes
The Powerware 9395 UPS supports a critical load in three different modes of operation. The UPS
can automatically use all three modes, as required. The standard operation modes are:
In Normal mode, the critical load is supplied by the inverter, which derives its power from
rectified utility AC power. In this mode, the battery charger also provides charging current
for the battery, if needed.
In Battery mode, the battery provides DC power, which maintains inverter operation. The
battery supports the critical load.
In Bypass mode, the critical load is directly supported by utility power. The following
paragraphs describe the differences in the three UPS operating modes, using block
diagrams to show the power flow during each mode of operation.
4.2.1 Normal mode
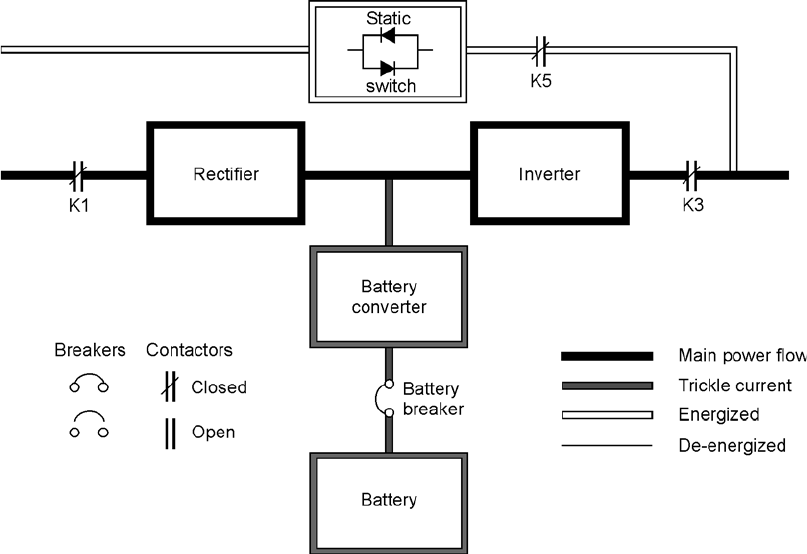
Figure 4-2 shows the path of electrical power through the UPS system when the UPS is
operating in normal mode.
Figure 4-2. Path of current through the UPS in normal mode
During normal UPS operation, power for the system is derived from a utility input source
through the rectifier input contactor K1. The front panel displays “Normal,” indicating the
incoming power is within voltage and frequency acceptance windows. Three-phase AC input
power is converted to DC using IGBT devices to produce a regulated DC voltage to the inverter.
The battery is charged directly from the regulated rectifier output through a buck or boost DC
converter, depending on whether the system voltage and the size of the battery string attached
to the unit.
The battery converter derives its input from the regulated DC output of the rectifier and
provides either a boosted or bucked regulated DC voltage charge current to the battery. The
battery is always connected to the UPS and ready to support the inverter should the utility input
become unavailable.
•
•
•